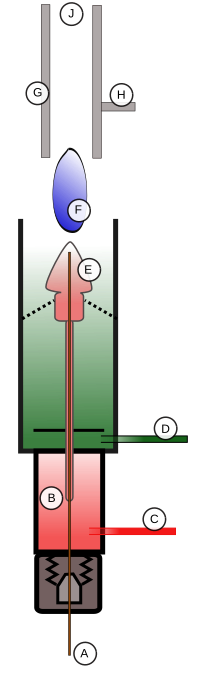
Flame Ionization Detector
Autor/Urheber:
Shortlink:
Quelle:
Größe:
200 x 700 Pixel (25085 Bytes)
Beschreibung:
Schematic of Flame Ionization Detector to match Wikipedia entry.
The eluent exits the GC column (A) and enters the FID detector’s oven (B). The oven is needed to make sure that as soon as the eluent exits the column, it does not come out of the gaseous phase and deposit on the interface between the column and FID. This deposition would result in loss of effluent and errors in detection. As the eluent travels up the FID, it is first mixed with the hydrogen fuel (C) and then with the oxidant (D). The effluent/fuel/oxidant mixture continues to travel up to the nozzle head where a positive bias voltage exists (E). This positive bias helps to repel the reduced carbon ions created by the flame (F) pyrolyzing the eluent. The ions are repelled up toward the collector plates (G) which are connected to a very sensitive ammeter, which detects the ions hitting the plates, then feeds that signal (H) to an amplifier, integrator, and display system. The products of the flame are finally vented out of the detector through the exhaust port (J).
Lizenz:
Public domain
Relevante Artikel
FlammenionisationsdetektorDer Flammenionisationsdetektor – kurz FID – ist ein Detektor für organische Verbindungen, der überwiegend in Verbindung mit Gaschromatographen (GC) eingesetzt wird. Weitere Einsatzgebiete des FID sind die Abwasserüberwachung auf flüchtige kohlenwasserstoffhaltige Substanzen, die Überwachung der Methangasemission auf Deponien sowie die Raum- und Außenluftüberwachung auf Kohlenwasserstoffe. .. weiterlesen