Trouton–Noble experiment
Autor/Urheber:
Trouton, F. T. and H. R. Noble
Shortlink:
Quelle:
Größe:
357 x 604 Pixel (19959 Bytes)
Beschreibung:
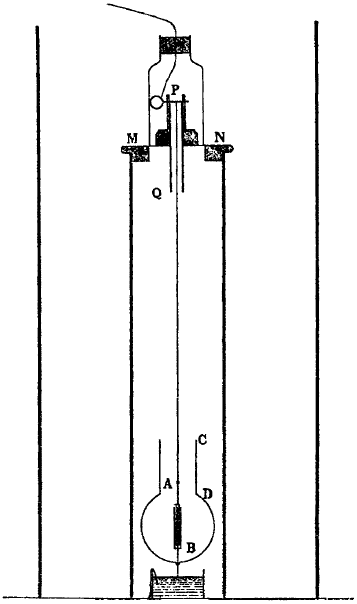
A circular capacitor B, 7.7 cm in diameter, built from multiple layers of mica and tinfoil, was fitted into a smooth spherical celluloid ball D that was covered with conductive paint, and which was suspended by a fine phosphor-bronze wire 37 cm long within a grounded tube. The wire was connected to one electrode of a Wimshurst machine which kept alternate plates of the capacitor charged to 3000 volts. The opposite plates of the capacitor as well as the celluloid ball were kept at ground voltage by means of a platinum wire that dipped into a sulfuric acid bath that not only served as a conductive electrode, but also damped oscillations and acted as a desiccant. A mirror attached to the capacitor was viewed through a telescope and allowed fine changes in orientation to be viewed.
Lizenz:
Public domain
Credit:
The Magnetic Forces Acting on a Charged Electric Condenser, Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London A 202, 165-181 (1903)
Relevante Bilder
Relevante Artikel
Trouton-Noble-ExperimentMit dem Trouton-Noble-Experiment versuchten Frederick Thomas Trouton und Henry R. Noble im Jahr 1903, den Bewegungszustand der Erde relativ zum Äther auf eine andere Art als beim Michelson-Morley-Experiment zu messen. Der negative Ausgang des Experiments war neben dem Michelson-Morley-Experiment eins der wichtigsten Gegenargumente gegen die Äthertheorie und wurde damit zu einer frühen Bestätigung der speziellen Relativitätstheorie. Es wurde mehrmals mit demselben Resultat wiederholt. .. weiterlesen