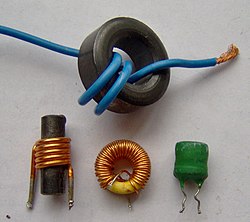
Toroidal inductor
The toroidal shape of the core further enhances the performance of the inductor. Unlike other core shapes, a toroid provides a closed-loop path for the magnetic flux, which significantly reduces magnetic flux leakage. This closed-loop configuration results in a higher inductance per unit volume compared to other core shapes, such as solenoids or cylindrical cores. Additionally, the toroidal shape allows for better control over the inductor’s magnetic field, making it ideal for applications requiring high efficiency and minimal electromagnetic interference, such as in power supplies, radio frequency (RF) circuits, and signal filtering.
In practical applications, the process of winding the wire around the toroidal ferrite core must be precise to achieve the desired inductance and performance characteristics. The number of turns of wire, the gauge of the wire, and the properties of the ferrite material all play crucial roles in determining the inductor’s characteristics. Engineers often use specific winding techniques to optimize the inductor’s performance, ensuring that it meets the required specifications for its intended application. The resulting inductor is a critical component in modern electronic devices, providing essential functions such as energy storage, filtering, and impedance matching, all while maintaining efficiency and reducing unwanted electromagnetic interference.Relevante Bilder
Relevante Artikel
Drossel (Elektrotechnik)Drosseln sind Spulen bzw. Induktivitäten zur Begrenzung von Strömen in elektrischen Leitungen, zur Zwischenspeicherung von Energie in Form ihres Magnetfeldes, zur Impedanzanpassung oder zur Filterung. Im Gegensatz zu Transformatoren oder Schwingkreis-Induktivitäten sind sie üblicherweise in Reihe zu anderen Bauteilen oder den Verbrauchern geschaltet. .. weiterlesen
RingkernAls Ringkern bezeichnet man unter anderem einen magnetischen Kreis in Ringform. Aus geometrischer Sicht sind dies Toroide, Ronden, Rohrabschnitte bzw. kreisrunde Körper mit einem Loch in der Mitte. Zusammen mit Wicklungen bildet er ein induktives Bauteil wie z. B. eine Ringkernspule oder Ringkerntransformator. .. weiterlesen
InduktivitätInduktivität ist eine Eigenschaft elektrischer Stromkreise oder Bauelemente, insbesondere von Spulen. Auf ihr beruht der Vorgang der Induktion, der eine Wechselwirkung zwischen Magnetismus und Elektrizität darstellt. Es ist zu unterscheiden zwischen Selbstinduktivität und Gegeninduktivität; mit „Induktivität“ ohne Zusatz ist fast immer die Selbstinduktivität gemeint. Die Selbstinduktivität eines Stromkreises setzt die zeitliche Änderungsrate des elektrischen Stroms mit der elektrischen Spannung in Beziehung:. .. weiterlesen