NGC660 - Gemini1210a
Credit:
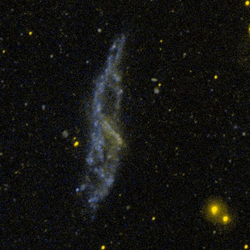
"This Gemini North telescope image captures the “bloody” aftermath of one galaxy piercing the heart of another. All the action appears in a single frame, with the stunning polar-ring galaxy NGC 660 as the focus of attention. NGC 660 spans some 40,000 light years across and lies about 40 million light years distant in the direction of the constellation of Pisces. It has an unusually high gas content and resolves into hundreds of objects, a considerable fraction of which are blue and red supergiant stars. The ring’s youngest detected stars formed only about seven million years ago, indicating a long and ongoing process of formation. As NGC 660’s ring is not truly polar, but inclined ~45˚ from the plane of the disk, it most likely formed by a previous interaction with a gas-rich galaxy about a billion years ago. That event would have stripped the interloper of its gas, directed it into NGC 660’s core, and triggered a furious burst of star formation. When the resulting short-lived, massive stars exploded shortly thereafter as supernovae, they would have generated shock waves that triggered more star formation, and so on, even to this day. " This image of the ring galaxy NGC 660, obtained with the Gemini Multi-Object Spectrograph on the Fredrick C. Gillett Gemini North telescope was obtained in August of 2012. The image is made from three images taken through g, r, i, and hydrogen alpha filters and assigned the colors of blue, green, orange and red respectively in this color composite image. The field of view is 9.3x5.6 arcminutes and it is oriented 8 degrees clockwise from north at right and east up. The total exposure (integration) time is 1,620 seconds for all filters. Color composite produced by Travis Rector, University of Alaska Anchorage.
Credit:
International Gemini Observatory/AURAThis media was created by the National Optical-Infrared Astronomy Research Laboratory (NOIRLab).
Their website states: "Unless specifically noted, the images, videos, and music distributed on the public NOIRLab website, along with the texts of press releases, announcements, images of the week and captions; are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, and may on a non-exclusive basis be reproduced without fee provided the credit is clear and visible." To the uploader: You must provide a link (URL) to the original file and the authorship information if available. | |
Diese Datei ist lizenziert unter der Creative-Commons-Lizenz „Namensnennung 4.0 international“.
| |
Relevante Bilder
Relevante Artikel
NGC 660NGC 660 ist eine aktive Balken-Spiralgalaxie mit hoher Sternentstehungsrate im Sternbild Fische auf der Ekliptik, die etwa 42 Millionen Lichtjahre von der Milchstraße entfernt ist. NGC 660 ist eine der wenigen Polarring-Galaxien. .. weiterlesen