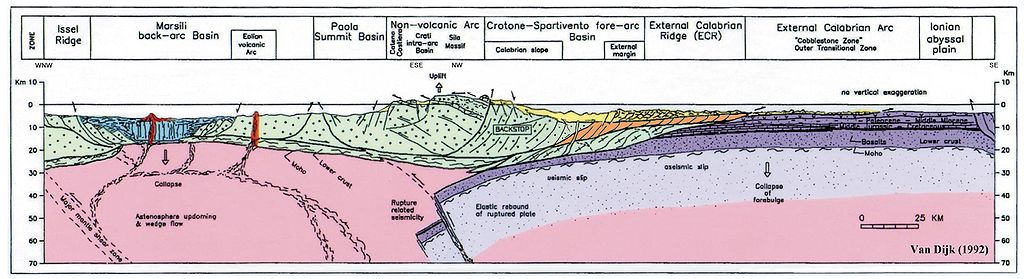
CalabrianArc-GeotectonicSection
All authors reproducing this figure in their work in original or modified form are kindly requested to correctly refer to the original source according to standard scientific ethics codes.
It is an original compilation of the present knowledge regarding this complex system, and numerous references and discussions regarding previous knowledge can be found in the extensive bibliographies of van Dijk & Okkes (1990), van Dijk (1992) and van Dijk et al. (2000).
The legend of the colours and the position of the section trace can be found on the map of the Central Mediterranean: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:CentralMediterranean-GeotectonicMap.jpg
It shows the overthrusting of the Calabrian Block also called "Calabrian Element", representing the southern Apennines and the Sicilian Maghrebides, of the promontory of the African Plate, the Ionian Sea. Furthermore the Tyrrhenian back-arc basin is shown with its recent volcanic arcs and tectonic stretching. It is underlined here that the internal structure of this Calabrian Block is only generally indicated in this figure; it is composed of a complex nappes pile dissected and deformed by transpressional fault zones, all generated during Late Eocene up to mid Pleistocene deformation phases. More details of this complex internal structure are depicted in the copyright protected figures of Van Dijk et al. (2000), which hopefully will soon become available in Wikipedia.
It can be appreciated that the Calabrian Block is moving towards the southeast along a detachment plane situated at a depth of around 15 to 25 km which dips to the southeast, and therefore suggests an important component of gravitational forces guiding the sliding of this lithosphere element, as underlined by many researchers in the past, and more recently revisited in the scientific literature. How these gravitational forces may interact and alternate with interplate and intraplate stress components related to the regional plate movements in the central Mediterranean is extensively discussed in van Dijk and Okkes (1991) and later works.
Domains that can be recognised include the Issel Ridge, The Marsili Basin, the Paola Basin, the Crotone Basin, also called Spartivento Basin, the external Calabrian Arc and the Ionian Abyssal Plain.
The rupture of the subducted slab below the arc and its consequences in terms of isostatic restablisation, astenospheric wedging and other, can be appreciated. These are all extensively discussed in van Dijk and Okkes (1990) and van Dijk and Scheepers (1995).
Another important phenomenon that is underlined in the figure is the incipient, start of subduction, of the Tyrrhenian crust, with a vergence of contraction towards the inner margin of the Arc, first proposed by van Dijk & Okkes (1990, 1991) and recently recognized also in other Mediterranean margins such as western North Africa.
References:
van Dijk, J.P., and Okkes, F.W.M. (1988); The analysis of shear zones in Calabria. implications for the geodynamics of the Central Mediterranean. La Ricerca Scient., Suppl., 68, 24-27.
van Dijk, J.P., and Okkes, F.W.M. (1990); The analysis of shear zones in Calabria. implications for the geodynamics of the Central Mediterranean. Riv. Ital. Strat. Paleont., 96 (2-3), 241-270.
van Dijk, J.P., and Okkes, F.W.M. (1991); Neogene tectonostratigraphy and kinematics of Calabrian Basins. implications for the geodynamics of the Central Mediterranean. Tectonophysics, 196, 23-60.
van Dijk, J.P. (1992); Late Neogene fore-arc basin evolution in the Calabrian Arc (Central Mediterranean). Tectonic sequence stratigraphy and dynamic geohistory. With special reference to the geology of Central Calabria. Geologica Ultrajectina, 92, 288 pp.
van Dijk, J.P., and Scheepers, P.J.J. (1995); Neogene rotations in the Calabrian Arc. Implications for a Pliocene-Recent geodynamic scenario for the Central Mediterranean. Earth Sci. Rev., 39, 207-246.
van Dijk, J.P., Barberis, A., Cantarella, G., and Massa, E. (1998); Central Mediterranean Messinian basin evolution. Tectono-eustasy or eustato-tectonics? Annales Tectonicae, 12, n. 1-2, 7-27.
van Dijk, J.P., Bello, M., Brancaleoni, G.P., Cantarella, G., Costa, V., Frixa, A., Golfetto, F., Merlini, S., Riva, M., Toricelli, S., Toscano, C., and Zerilli, A. (2000); A new structural model for the northern sector of the Calabrian Arc. Tectonophysics, 324, 267-320.
van Dijk, J.P., Bello, M., Toscano, C., Bersani, A., and Nardon, S. (2000); Tectonic model and 3D fracture network analysis of Monte Alpi (Southern Apennines). Tectonophysics, 324, 203-237.Relevante Bilder
Relevante Artikel
KalabrienKalabrien ist die südlichste Region des italienischen Festlandes. Bildlich gesprochen nimmt es die Stiefelspitze der Italienischen Halbinsel ein. Es hat eine Fläche von 15.080 km² und 1.855.454 Einwohner. Die Hauptstadt der Region ist Catanzaro. .. weiterlesen