Titantetraethanolat
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Titantetraethanolat | ||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen | |||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C8H20O4Ti | ||||||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung | |||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 228,15 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand | fest | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dichte | |||||||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | |||||||||||||||||||
| Siedepunkt | |||||||||||||||||||
| Löslichkeit | hydrolysiert in Wasser[9] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brechungsindex | 1,505 (20 °C)[10] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. Brechungsindex: Na-D-Linie, 20 °C | |||||||||||||||||||
Titantetraethanolat ist eine chemische Verbindung aus der Gruppe der Alkoholate bzw. titanorganischen Verbindungen.
Eigenschaften
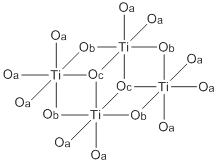
Titantetraethanolat ist ein weißer, kristalliner Feststoff, der bei 38–40 °C schmilzt.[7][3] Die Verbindung kommt auch als farblose bis gelbliche Flüssigkeit mit alkoholischem Geruch vor, wobei dies mit einer metastabilen unterkühlten Schmelze[2] oder durch Verunreinigungen durch Hydrolyseprodukte begründet werden kann.[3] Der Feststoff bildet ein monoklines Kristallgitter mit der Raumgruppe C2/c.[6] Dabei liegt eine tetramere Struktur vor, wobei die Titanatome oktaedrisch koordiniert sind. Für die Ethanolatfunktion gibt es drei verschiedene Bindungvarianten mit einfach, zweifach und dreifach koordiniertem Sauerstoffatom. Aus der unterschiedlichen Koordination resultieren verschiedene Ti-O-Bindungslängen.[6] In flüssiger Phase und in Lösung treten trimere Strukturen auf.[5][4][3][11]
Das Alkoholat hydrolysiert in Wasser und ist löslich in Toluol und Aceton.
Es besitzt eine Viskosität von 55 bis 65 mPa·s bei 20 °C.[9] Technisches Titantetraethanolat enthält 5 bis 15 % Isopropanol.[12]
Verwendung
Titantetraethanolat kann zur Herstellung von Titandioxid-Schichten und Nanopartikeln verwendet werden.[13]
Sicherheitshinweise
Die Dämpfe von Titantetraethanolat können mit Luft ein explosionsfähiges Gemisch (Flammpunkt 42 °C) bilden.[8]
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ Eintrag zu TITANIUM ETHOXIDE in der CosIng-Datenbank der EU-Kommission, abgerufen am 11. Dezember 2021.
- ↑ a b c Crowe, R.W.; Caughlan, C.N.: The Electric Moments of Tetraethoxytitanium, Monochlorotriethoxytitanium and Trichlorophenoxytitanium in Benzene Solutions. I in J. Am. Chem. Soc. 72 (1950) 1694–1697, doi:10.1021/ja01160a076.
- ↑ a b c d e Bradley, D.C.; Gaze, R.; Wardlaw, W.: The hydrolysis of titanium tetraethoxide in J. Chem. Soc. 1955, 721–726, doi:10.1039/JR9550000721.
- ↑ a b Bradley, D.C.; Prevedorou, C.C.A.; Swanwick, J.D.; Wardlaw, W.: Parachors and molecular structure of some metal alkoxides in J. Chem. Soc. 1958, 1010–1014, doi:10.1039/JR9580001010.
- ↑ a b Caughlan, C.N. Smith, H.S.; Katz, W.; Hodgson, W.; Crowe, R.W.: Organic Compounds of Titanium. II. Association of Organic Titanates in Benzene Solution in J. Am. Chem. Soc. 73 (1951) 5652–5654, doi:10.1021/ja01156a046.
- ↑ a b c Ibers, J.A.: Crystal and Molecular Structure of Titanium (IV) Ethoxide in Nature 197 (1963) 686–687, doi:10.1038/197686a0.
- ↑ a b Turevskaya, E.P.: Izvestiya Akademii Nauk SSSR, Seriya Khimicheskaya 1977, (7), 1463–1466.
- ↑ a b c d Eintrag zu Titantetraethanolat in der GESTIS-Stoffdatenbank des IFA, abgerufen am 1. Februar 2016. (JavaScript erforderlich)
- ↑ a b Datenblatt Titantetraethanolat bei Merck, abgerufen am 20. Februar 2010.
- ↑ Datenblatt Titanium(IV) ethoxide bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 24. April 2011 (PDF).
- ↑ Martin, R.L.; Winter, G.: Association of Titanium(IV) Alkoxides in Benzene in Nature 197 (1963) 687, doi:10.1038/197687a0.
- ↑ Eintrag zu Titan(IV) Ethoxid, 85 %, Tech., enthält 5–15 % Isopropanol bei Thermo Fisher Scientific, abgerufen am 22. September 2023.
- ↑ Nurul Huda Yusoff, Muhamad Mat Salleh, Muhammad Yahaya: Fluorescence gas sensor using TiO2 nanoparticles coated with porphyrin dye thin Films. In: Solid State Science and Technology, Vol. 16, No. 1 (2008) S. 63–74.
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) pictogram for flammable substances
Autor/Urheber: Tzaph, Lizenz: CC0
Chemische Struktur von Titan(IV)-ethanolat / TEOT / Titantetraethanolat
Autor/Urheber: Oh hey spec20, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
A partial structure of titanium(IV) ethoxide.




