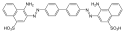Direktfarbstoffe
Substantive bzw. Direktfarbstoffe[1] sind Farbstoffe für Cellulose und Celluloseregenerat, beispielsweise Baumwolle, Jute, Viskose oder Papier, die im Gegensatz zu Reaktivfarbstoffen nur durch physikalische Wechselwirkungen (Van-der-Waals-Kräfte) an die Faser gebunden sind und folglich eine hohe Affinität zum Substrat besitzen müssen.[2]
Chemische Konstitution
Die Direktfarbstoffe kommen überwiegend aus der Gruppe der Azofarbstoffe, lediglich einige Dioxazinfarbstoffe, Phthalocyaninfarbstoffe und Nichtazo-Metallkomplexfarbstoffe haben darüber hinaus eine gewisse Bedeutung. Für die benötigte hohe Substantivität müssen die Farbstoffmoleküle koplanar aufgebaut sein und lange Ketten konjugierter Doppelbindungen aufweisen.[3]
Farbstoffe mit einer hohen Substantivität sind beispielsweise Azofarbstoffe mit 3,3'-disubstituierten Benzidinderivaten als Diazokomponente:
Trotz der guten substantiven Eigenschaften werden diese Farbstoffe aufgrund der karzinogenen Eigenschaften von Benzidin und verschiedenen Benzidinderivaten nicht mehr verwendet. Da die aus 2,2'-disubstituierten Benzidinderivaten hergestellten Azofarbstoffe aufgrund der sterischen Hinderung keine koplanare Struktur aufweisen, sind sie nicht ausreichend substantiv und nicht als Direktfarbstoffe geeignet.[3]
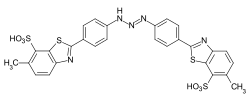
Eine gute Substantivität zeigen Farbstoffe mit einer Harnstoffstruktur. Durch Umsetzung vom aromatischen Aminen mit Phosgen erhält man symmetrische Diaryl-Harnstoffderivate, die als Kupplungskomponente mit einer Diazokomponente zu einem Bisazofarbstoff reagieren.
Beispiel:
Durch Umsetzung von I-Säure 1 mit Phosgen 2 erhält man das Zwischenprodukt I-Säure-Harnstoff[5] 3. Dieses kuppelt mit Diazoniumsalz 5, das man durch die Diazotierung von Anilin 4 erhält, zu dem Direktfarbstoff C.I. Direct Orange 26[6] 6.
Direktfärbung
Bei der Direktfärbung wird das zu färbende Substrat in eine wässrige Lösung der Direktfarbstoffe, die sogenannte Färbeflotte, eingebracht. Die hohe Affinität der Farbstoffe bewirkt, dass diese in der Regel direkt auf die Faser aufziehen (daher die Bezeichnung Direktfarbstoffe). Das Mengenverhältnis des Farbstoffes im Färbegut zu dem in der Flotte, der sogenannte Ausziehgrad, kann durch Salzzugabe und/oder pH-Wert-Änderungen beeinflusst werden. Gute Substantivfarbstoffe mit einer hohen Substantivität erreichen dabei einen Ausziehgrad von > 99 %, d. h. die Färbeflotte ist nach der Färbung fast farblos.
Vorteil der Direktfarbstoffe ist deren sehr einfaches Färbeverfahren, Nachteile dagegen die im Vergleich zu den Reaktivfarbstoffen deutlich schlechtere Nassechtheit: Substantiv gefärbte Textilien können auch nach mehrmaliger Wäsche noch „bluten“ und damit auf mitgewaschene andere Textilien abfärben.
Beispiele
| C.I. Name | C.I. Nr. | CAS-Nr. | sonstige Namen | Struktur | Farbe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Yellow 1 | 22250 | 6472-91-9 | Chrysamin G |  | |
| Direct Yellow 9 | 19540 | 1829-00-1 | Thiazolgelb |  | |
| Direct Yellow 7 Direct Yellow 59 | 49010 | 8064-60-6 | Primulin |  | |
| Direct Yellow 11 | 40000 | 1325-37-7 | Direct Yellow R | ||
| Direct Yellow 12 | 24895 | 2870-32-8 | Chrysophenin |  | |
| Direct Yellow 27 | 13950 | 10190-68-8 | Direct Fast Yellow 5GL |  | |
| Direct Yellow 28 | 19555 | 8005-72-9 | Chloramingelb |  | |
| Direct Yellow 44 | 29000 | 8005-52-5 | Direct Fast Yellow L4G |  | |
| Direct Yellow 50 | 29025 | 3214-47-9 | Direct Fast Yellow RS |  | |
| Direct Yellow 86 | 29325 | 50925-42-3 | Direct Fast Yellow RL |  | |
| Direct Yellow 96 | 61725-08-4 | Direct Fluorescent Light Yellow 7GFF Diphenyl Brilliant Flavin | |||
| Direct Yellow 106 | 40300 | 12222-60-5 | Direct Fast Yellow L3R | 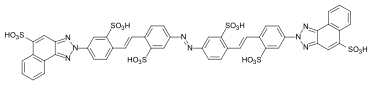 | |
| Direct Yellow 120 | 29040 | 12222-63-8 | Direct Fast Yellow GR |  | |
| Direct Yellow 142 | 71902-08-4 | Direct Fast Yellow PG | 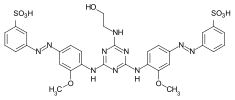 | ||
| Direct Yellow 147 | 71838-49-8 | Direct Fast Yellow GL |  | ||
| Direct Orange 26 | 29150 | 3626-36-6 | Direct Orange S |  | |
| Direct Orange 34 | 40220 | 12222-37-6 | Direct Fast Orange 7GL | ||
| Direct Orange 39 | 40215 | 1325-54-8 | Direct Light Fast Orange 4GL |  | |
| Direct Brown 1 | 30045 | 3811-71-0 | Direct Brown D3G |  | |
| Direct Brown 2 | 22311 | 2429-82-5 | Direct Brown M / MM |  | |
| Direct Brown 210 | 22312 | 12222-29-6 | Direct Fast Brown GTL | ||
| Direct Red 2 | 23500 | 992-59-6 | Benzopurpurin |  | |
| Direct Red 13 | 22155 | 1937-35-5 | Direct Red B Direct Bordeaux | 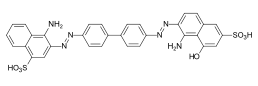 | |
| Direct Red 16 | 27680 | 6227-02-7 | Direct Light Fast Red 6B |  | |
| Direct Red 28 | 22120 | 573-58-0 | Kongorot |  | |
| Direct Blue 1 | 24410 | 2610-05-1 | Chicagoblau 6B Diaminreinblau FF |  | |
| Direct Blue 6 | 22610 | 2602-46-2 | Direct Blue 2BA |  | |
| Direct Blue 14 | 23850 | 72-57-1 | Trypanblau 3B Benzaminblau | 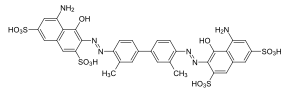 | |
| Direct Blue 71 | 34149 | 4399-55-7 | Sirius Blau S-BRR |  | |
| Direct Blue 199 | 74190 | 12222-04-7 | Direct Blue FBL | ||
| Direct Green 1 | 30280 | 3626-28-6 | Direct Dark Green |  | |
| Direct Green 6 | 30295 | 4335-09-5 | Direct Green B |  | |
| Direct Black 38 | 30235 | 1937-37-7 | Direkttiefschwarz E |  |
CAS-Nr.: Na-Salz / Strukturen: freie Säure
Siehe auch
- Beizenfarbstoffe (C.I. Mordant Dyes)
- Dispersionsfarbstoffe (C.I. Disperse Dyes)
- Kationische Farbstoffe (C.I. Basic Dyes)
- Küpenfarbstoffe (C.I. Vat Dyes)
- Lösungsmittelfarbstoffe (C.I. Solvent Dyes)
- Reaktivfarbstoffe (C.I. Reactive Dyes)
- Säurefarbstoffe (C.I. Acid Dyes)
Weblinks
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ Hans Beyer, Wolfgang Walter: Lehrbuch der organischen Chemie. 18. Auflage. S. Hirzel Verlag, Stuttgart 1978, ISBN 3-7776-0342-2, S. 517–519.
- ↑ H. Bach, E. Pfeil, W. Philippar, M. Reich: Molekülbau und Haftung substantiver Farbstoffe auf Cellulose. In: Angewandte Chemie. Band 75, Nr. 9, 7. Mai 1963, S. 407–416, doi:10.1002/ange.19630750903.
- ↑ a b Klaus Hunger (Hrsg.): Industrial Dyes: Chemistry, Properties, Applications. WILEY-VCH Verlag, Weinheim 2003, ISBN 978-3-662-01950-4, S. 158 ff. (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- ↑ Externe Identifikatoren von bzw. Datenbank-Links zu Direct Blue 8: CAS-Nummer: 2429-71-2, EG-Nummer: 219-382-7, ECHA-InfoCard: 100.017.621, PubChem: 17055, ChemSpider: 16735697, Wikidata: Q27254953.
- ↑ Externe Identifikatoren von bzw. Datenbank-Links zu I-Säure-Harnstoff: CAS-Nummer: 134-47-4, EG-Nummer: 205-142-9, ECHA-InfoCard: 100.004.676, PubChem: 67254, ChemSpider: 60588, Wikidata: Q27074444.
- ↑ Externe Identifikatoren von bzw. Datenbank-Links zu C.I. Direct Orange 26 (Di-Natriumsalz): CAS-Nummer: 3626-36-6, EG-Nummer: 222-838-8, ECHA-InfoCard: 100.020.763, PubChem: 77182, ChemSpider: 21171947, Wikidata: Q72469576.
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
Autor/Urheber: DiplomBastler alias Torge Anders, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
Bild zur Prüfung der Farbdarstellung (Gammakorrektur der Farbkanäle) des Anzeigegeräts ("Bildschirm"). Eine Beschreibung, wie man das Bild verwendet, ist Hilfe:Farbdarstellung. Eine Beschreibung der Wirkungsweise des Bildes findet sich hier. Es existiert auch eine vektorisierte Version des Bildes, die jedoch, wie *alle* Vektorformate, *nicht* zur Kalibrierung geeignet ist. Näheres dazu siehe Vorlage_Diskussion:Hinweis_Farbdarstellung#Vektorgrafik_kann_hier_nicht_funktionieren. Bitte daher diese Raster-Version hier nicht durch eine Vektor-Version ersetzen.
Struktur von Kongorot
chemical structure of C.I. Direct Green 6 (free acid)
chemical structure of C.I. Direct Blue 71 (free acid)
Chemical structure of C.I. Direct Yellow 9 (free acid)
chemical structure of C.I. Direct Brown 2 (free acid)
Chemical structure of C.I. Direct Red 2 (free acid)
Chemical structure of C.I. Direct Yellow 1 (free acid)
chemical structure of C.I. Direct Blue 8
chemical structure of C.I. Direct Yellow 86 (free acid)
Die Strukturformel von Trypanblau
chemical structure of C.I. Direct Green 1 (free acid)
chemical structure of C.I. Direct Orange 26 (free acid)
chemical structure of C.I. Direct Yellow 50 (free acid)
chemical structure of C.I. Direct Yellow 28 (free acid)
chemical structure of C.I. Direct Black 38 (free acid)
chemical structure of C.I. Direct Blue 6 (free acid)
chemical structure of C.I. Direct Yellow 120 (free acid)
chemical structure of C.I. Direct Red 13 (free acid)
chemical structure of C.I. Direct Yellow 147 (free acid)
Chemical structure of C.I. Direct Blue 1 (free acid)
Chemical structure of C.I. Direct Yellow 59 (free acid)
chemical structure of C.I. Direct Yellow 106 (free acid)
chemical structure of C.I. Direct Yellow 27 (free acid)
chemical structure of Direct Red 16 (free acid)
chemical structure of C.I. Direct Yellow 142 (free acid)
Synthesis of C.I. Direct Orange 26 starting from J-Acid, Phosgene and Aniline
chemical structure of C.I. Direct Yellow 12 (free acid)
chemical structure of C.I. Direct Yellow 44 (free acid)
chemical structure of C.I. Direct Orange 39 (free acid)
chemical structure of C.I. Direct Direct Brown 1 (free acid)