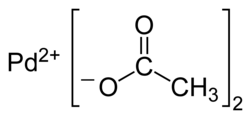
Palladium(II)-acetat
| Strukturformel | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | ||||||||||||||||
| Name | Palladium(II)-acetat | |||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen | Pd(OAc)2 | |||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | Pd(OCOCH3)2 | |||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung | Feststoff[1] | |||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | ||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 224,51 g·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand | fest[1] | |||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | ||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | ||||||||||||||||
Palladium(II)-acetat ist eine chemische Verbindung des Palladiums mit der Halbstrukturformel Pd(CH3COO)2. Palladium(II)-acetat löst sich in vielen organischen Lösungsmitteln und wird als Katalysator für organische Synthesen genutzt. In der metallorganischen Chemie dient es als Präkursor für andere Palladium-Komplexe.
Herstellung
Palladium(II)-acetat kann durch Reaktion von Palladiummetall mit einem Gemisch aus heißer Salpetersäure und Essigsäure hergestellt werden. Je nach Herstellung kann Palladium(II)-acetat als braunes Pulver mit einer trimeren Struktur oder als rosafarbenes Pulver mit einer Kettenstruktur vorliegen.[2][3]
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ a b c d e Datenblatt Palladium(II) acetate, ≥99.9% trace metals basis bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 16. Juli 2017 (PDF).
- ↑ T. A. Stephenson, S. M. Morehouse, A. R. Powell, J. P. Heffer, G. Wilkinson: 667. Carboxylates of palladium, platinum, and rhodium, and their adducts. In: Journal of the Chemical Society. 1965, S. 3632–3640, doi:10.1039/JR9650003632.
- ↑ Sergei D. Kirik, Ruslan F. Mulagaleev, Alexander I. Blokhin: [Pd(CH3COO)2] from X-ray powder diffraction data. In: Acta Crystallographica Section C Crystal Structure Communications. 60, 2004, S. m449–m450, doi:10.1107/S0108270104016129.
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) pictogram for corrosive substances
Diagram of the structural formulae of the constituent ions of palladium(II) acetate, Pd(OAc)2.
For the actual structure of the substance when solid, see Category:Crystal structures of palladium(II) acetate.
Structure drawn in ChemBioDraw Ultra 12.0.

