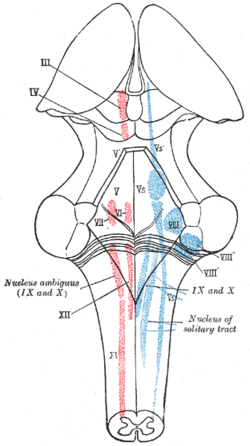
Nucleus ambiguus

Der Nucleus ambiguus ist eine Ansammlung von Nervenzellen (Kerngebiet) im Bereich des Tegmentum der Medulla oblongata.
Er ist ein viszeromotorischer Kern, dessen Axone über die Hirnnerven Nervus glossopharyngeus, Nervus vagus und Nervus accessorius das Gehirn verlassen. Die Nervenzellen steuern damit Muskeln des Gaumens, des Rachens und des Kehlkopfs an.[1]
Der Nucleus ambiguus ist als viszeromotorischer Hirnnervenkern Ausgangspunkt für efferente, myelinisierte Nervenfasern der zuvor genannten Hirnnerven.[2]
Afferenzen erhält der Nucleus ambiguus über den Tractus corticonuclearis aus der Großhirnrinde sowie aus dem Nucleus spinalis nervi trigemini.
Literatur
- Mark Buchta: Das Physikum. Kompendium zum 1. Abschnitt der ärztlichen Prüfung. 2. Auflage. Elsevier, Urban & Fischer, München 2010, ISBN 978-3-437-43051-0, S. 214.
- Wolf-Georg Forssmann, Christian Heym: Neuroanatomie. 3. Auflage, Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg/New York 1982, ISBN 3-540-11404-1
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ Alfred Benninghoff: Makroskopische und mikroskopische Anatomie des Menschen. Band 3, 13./14. Auflage, Urban & Schwarzenberg, München/Wien/Baltimore 1985, ISBN 3-541-00264-6, S. 428
- ↑ Dee U. Silverthorn: Physiologie. 4. Auflage, Pearson, München 2009, ISBN 978-3-8273-7333-5, S. 543
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
The formatio reticularis of the medulla oblongata, shown by a transverse section passing through the middle of the olive. (Testut.) 1. Anterior median fissure. 2. Fourth ventricle. 3. Formatio reticularis, with 3’, its internal part (reticularis alba), and 3’’, its external part (reticularis grisea). 4. Raphe. 5. Pyramid. 6. Lemniscus. 7. Inferior olivary nucleus with the two accessory olivary nuclei. 8. Hypoglossal nerve, with 8’, its nucleus of origin. 9. Vagus nerve, with 9’, its nucleus of termination. 10. Lateral dorsal acoustic nucleus. 11. Nucleus ambiguus (nucleus of origin of motor fibers of glossopharyngeal, vagus, and cerebral portion of spinal accessory). 12. Gracile nucleus. 13. Cuneate nucleus. 14. Head of posterior column, with 14’, the lower sensory root of trigeminal nerve. 15. Fasciculus solitarius. 16. Anterior external arcuate fibers, with 16’, the nucleus arcuatus. 17. Nucleus lateralis 18. Nucleus of fasciculus teres. 19. Ligula (medullary insertion of the tectorial membrane).

