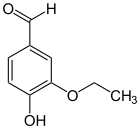
Novovanillin
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Novovanillin | ||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C9H10O3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 166,17 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand | fest | ||||||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | |||||||||||||||||||
| Siedepunkt | 263–264 °C[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen (0 °C, 1000 hPa). | |||||||||||||||||||
Novovanillin (3-Ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzaldehyd, ortho-Ethylvanillin) ist eine organische chemische Verbindung mit der Summenformel C9H10O3. Es ist ein Derivat des Benzaldehyds mit einer zusätzlichen Hydroxy- und einer Ethoxygruppe. Die Hydroxygruppe steht hier, wie beim ortho-Vanillin, in ortho-Stellung zur Aldehydgruppe. Im Ethylvanillin befinden sich diese beiden Gruppen in para-Stellung.
Novovanillin ist ein Feststoff, schmilzt bei 66–68 °C und siedet bei 263–264 °C.[1]
Es sind vierwertige Vanadiumkomplexe (mit VO2+) der Formel [V(IV)O (dsal)2 (H2O)] mit ortho-hydroxysubstituierten Benzaldehyden bekannt (mit Hdsal = Salicylaldehyd, ortho-Vanillin bzw. Novovanillin).[2]
Literatur
- Elmar Profft: „Zur Kenntnis des o-Vanillins und des Novovanillins (= 2-Oxy-3-äthoxybenzaldehyd-1). I“, in: Journal für Praktische Chemie, 1957, 5 (3–4), S. 175–181; doi:10.1002/prac.19570050303.
- Elmar Profft, Peter Märker: „Zur Kenntnis des o-Vanillins und des Novovanillins (= 2-Oxy-3-äthoxybenzaldehyd-1). IV“, in: Journal für Praktische Chemie, 1959, 8 (3–4), S. 199–206; doi:10.1002/prac.19590080311.
- Elmar Profft: „Data on the ortho- & novovanillins (2-hydroxy-3-ethoxybenzaldehyde-1)“, in: Arzneimittel-Forschung, 1959, 9 (3), S. 157–161; PMID 13651025.
- Elmar Profft: „Data on o-vanillin & novovanillin (2-hydroxy-3-ethoxybenzaldehyde). II. Preparation of 2,3-dialkoxyphenyl-beta-ethylamine“, in: Archiv der Pharmazie und Berichte der Deutschen Pharmazeutischen Gesellschaft, 1959, 292 (2), S. 70–75, PMID 13650594.
- E. Profft, K. Stühmer: „Benzoins, benzils and benzilic acids of o-vanillin- and o-novovanillin ether“, in: Archiv der Pharmazie und Berichte der Deutschen Pharmazeutischen Gesellschaft, 1965, 298 (10), S. 677–685; PMID 5222289.
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ a b c d e Datenblatt 3-Ethoxysalicylaldehyde bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 16. April 2011 (PDF).
- ↑ J. C. Pessoa, I. Cavaco, I. Correia, I. Tomaz, T. Duarte, P. M. Matias: „Oxovanadium(IV) complexes with aromatic aldehydes“, in: J. Inorg. Biochem., 2000, 80 (1–2), S. 35–39; PMID 10885461.
Weblinks
- Eintrag zu Novovanillin. In: P. J. Linstrom, W. G. Mallard (Hrsg.): NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69. National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg MD, abgerufen am 14. Dezember 2012.
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
Struktur von Ethylvanillin
Struktur des o-Vanillin
s.o.; 3-Ethoxysalicylaldehyd; 3-Ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzaldehyd