Messier 96
| Galaxie Messier 96 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Aufnahme des Very Large Telescopes | |
| AladinLite | |
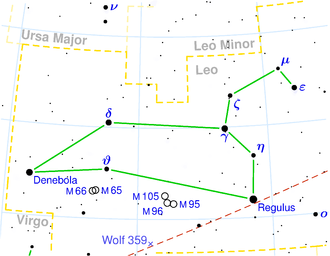
| Sternbild | Löwe |
| Position Äquinoktium: J2000.0, Epoche: J2000.0 | |
| Rektaszension | 10h 46m 45,7s[1] |
| Deklination | +11° 49′ 12″[1] |
| Erscheinungsbild | |
| Morphologischer Typ | SAB(rs)ab[1] |
| Helligkeit (visuell) | 9,2 mag[2] |
| Helligkeit (B-Band) | 10,1 mag[3] |
| Winkelausdehnung | 7′,8 × 5′,2[3] |
| Positionswinkel | 176°[3] |
| Flächenhelligkeit | 13,2 mag/arcmin²[3] |
| Physikalische Daten | |
| Zugehörigkeit | M96-Gruppe LGG 217[1][4] |
| Rotverschiebung | 0,002992 ± 0,000013[1] |
| Radialgeschwindigkeit | (897 ± 4) km/s[1] |
| Entfernung | 31 ± 3 Mio. Lj / 9,6 ± 1,0 Mio. pc [5] |
| Geschichte | |
| Entdeckung | Pierre Méchain |
| Entdeckungsdatum | 20. März 1781 |
| Katalogbezeichnungen | |
| M 96 • NGC 3368 • UGC 5882 • PGC 32192 • CGCG 66-13 • MCG +2-28-6 • IRAS 10441+1205 • 2MASX J10464574+1149117 • GC 2194 • h 749 • HIPASS J1046+11 | |
Messier 96 (auch als NGC 3368 katalogisiert) ist eine Balken-Spiralgalaxie vom morphologischen Typ SAB(rs)ab im Sternbild Löwe. Sie ist etwas über 30 Millionen Lichtjahre von der Milchstraße entfernt und besitzt eine ähnliche Größe und Masse wie diese. Zudem besitzt M96 einen aktiven Galaxienkern.
Die Galaxie ist Namensgeber der M96-Gruppe, zu der sich auch Messier 95, Messier 105 und einige kleinere und lichtschwächere Systeme gehören.
Die Entdeckung als nebliges Objekt gelang am 20. März 1781 dem Astronomen Pierre Méchain.[6]
- (c) ESA/Hubble, CC BY 4.0
Hochaufgelöste Aufnahme des Zentrums von Messier 96, erstellt mithilfe des Hubble-Weltraumteleskops
Aufnahme der Ultraviolettstrahlung von Messier 96 durch das Weltraumteleskop GALEX.
Weblinks
- Spektrum.de: Umgebungskarte
- A galactic maelstrom (engl.)
- astronews.com: Bild des Tages 1. September 2015
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ a b c d NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database
- ↑ De Laet, Rony (2012): The Casual Sky Observer's Guide: Stargazing with Binoculars and Small Telescopes. New York: Springer. S. 130.
- ↑ a b c d SEDS: NGC 3368
- ↑ VizieR
- ↑ Jensen, Joseph B. et al. (2003): Measuring Distances and Probing the Unresolved Stellar Populations of Galaxies Using Infrared Surface Brightness Fluctuations. In: Astrophysical Journal 583(2), S. 712–726.
- ↑ Seligman
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
Bildtafel der 110 Messier-Objekte. Diese Datei wird in der w:de:Template:Navigationsleiste Messierobjekte als Imagemap genutzt. Sie darf daher nicht durch eine andere Version überschrieben werden!
Autor/Urheber: Copyright © 2003 Torsten Bronger., Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
This is a celestial map of the constellation Leo, the Lion.
Autor/Urheber: ESO/Oleg Maliy, Lizenz: CC BY 3.0
Not all spiral galaxies have to be picture-perfect to be striking. Messier 96, also known as NGC 3368, is a case in point: its core is displaced from the centre, its gas and dust are distributed asymmetrically and its spiral arms are ill-defined. But this portrait, taken with the FORS1 instrument on ESO’s Very Large Telescope, shows that imperfection is beauty in Messier 96. The galaxy's core is compact but glowing, and the dark dust lanes around it move in a delicate swirl towards the nucleus. And the spiral arms, patchy rings of young blue stars, are like necklaces of blue pearls.
Messier 96 lies in the constellation of Leo (The Lion). It is the largest galaxy in the Leo I group of galaxies; including its outermost spiral arms, it spans some 100 000 light-years in diameter — about the size of our Milky Way. Its graceful imperfections likely result from the gravitational pull of other members in the group, or are perhaps due to past galactic encounters.
A multitude of background galaxies peers through the dusty spiral. Perhaps the most striking of these objects is an edge-on galaxy that — because of a chance alignment — appears to interrupt the outermost spiral arm to the upper left of Messier 96's core.
This image was processed by ESO using the observational data found by Oleg Maliy from Ukraine, who participated in ESO's Hidden Treasures 2010 astrophotography competition [1], organised in October–November 2010, for everyone who enjoys making beautiful images of the night sky using astronomical data obtained with professional telescopes. The image was made with data taken at visible and infrared wavelengths through B, V, and I filters.
Notes
[1] ESO’s Hidden Treasures 2010 competition gave amateur astronomers the opportunity to search through ESO’s vast archives of astronomical data, hoping to find a well-hidden gem that needed polishing by the entrants. To find out more about Hidden Treasures, visit http://www.eso.org/public/outreach/hiddentreasures/.(c) ESA/Hubble, CC BY 4.0
This new NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope shows Messier 96, a spiral galaxy just over 35 million light-years away in the constellation of Leo (The Lion). It is of about the same mass and size as the Milky Way. It was first discovered by astronomer Pierre Méchain in 1781, and added to Charles Messier’s famous catalogue of astronomical objects just four days later.
The galaxy resembles a giant maelstrom of glowing gas, rippled with dark dust that swirls inwards towards the nucleus. Messier 96 is a very asymmetric galaxy; its dust and gas is unevenly spread throughout its weak spiral arms, and its core is not exactly at the galactic centre. Its arms are also asymmetrical, thought to have been influenced by the gravitational pull of other galaxies within the same group as Messier 96.
This group, named the M96 Group, also includes the bright galaxies Messier 105 and Messier 95, as well as a number of smaller and fainter galaxies. It is the nearest group containing both bright spirals and a bright elliptical galaxy (Messier 105).