Monolignole
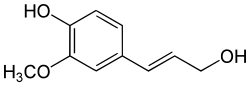
Als Monolignole bezeichnet man p-Cumarylalkohol (H), Coniferylalkohol (G) und Sinapylalkohol (S). Diese sind die Monomere, aus welchen sich das Biopolymer Lignin zusammensetzt. p-Cumarylalkohol, Coniferylalkohol und Sinapylalkohol sind hydroxylierte Phenylpropanoide, die sich in der Anzahl an Methoxy-Substituenten am Ring unterscheiden.[1][2] Die in der Literatur als Abkürzung verwendeten Buchstaben beziehen sich auf die jeweiligen Grundstrukturen ohne die Propenylgruppe, also Hydroxybenzol (H), Guajacol (G) und Syringol (S).
| Monolignole | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Struktur: |  |  |  |
| Bezeichnung: | Cumarylalkohol | Coniferylalkohol | Sinapylalkohol |
| IUPAC: | 4-[(1E)-3-Hydroxy-1-propen-1-yl]phenol | 4-[(1E)-3-Hydroxy-1-propen-1-yl]-2-methoxyphenol | 4-[(1E)-3-Hydroxy-1-propen-1-yl]-2,6-dimethoxyphenol |
| CAS-Nr.: | 20649-40-5 | 32811-40-8 | 537-33-7 |
| Wikidata.: | Q420084 | Q418993 | Q418975 |
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ Wout Boerjan, John Ralph, Marie Baucher: Lignin Biosynthesis. In: Annual Review of Plant Biology. Band 54, Nr. 1, Juni 2003, S. 519–546, doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.54.031902.134938, PMID 14503002.
- ↑ Eintrag zu Lignin. In: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, abgerufen am 6. April 2022.
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
Coniferylalkohol
Cumarylalkohol; p-Cumarsäure
Sinapylalkohol