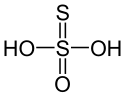
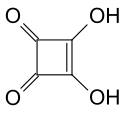
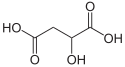
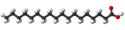Liste von Säuren
Die folgende Liste zeigt eine Auswahl von Säuren. Aufgelistet sind
- der gebräuchliche Trivialname
- der IUPAC-Name (die offizielle Bezeichnung)
- die Summenformel oder eine vereinfachte Strukturformel
Die Liste erhebt keinen Anspruch auf Vollständigkeit.
Anorganische Säuren (Auswahl)
Säuren der Edelgase
| Element | Oxidationszustand des Zentralatomes | Trivialname | Formel | Salze |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xenon | +6 | Xenonsäure | Xenate | |
| +8 | Perxenonsäure | Perxenate |
Säuren der Halogene
| Element | Oxidationszustand des Halogenatomes | Trivialname | Formel | Salze | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluor | −1 | Flusssäure | Fluoride | Wässrige Lösung von Fluorwasserstoff | |
| −1 | Hypofluorige Säure | Hypofluorite | |||
| Chlor | −1 | Salzsäure | Chloride | Wässrige Lösung von Chlorwasserstoff | |
| +1 | Hypochlorige Säure | Hypochlorite | |||
| +3 | Chlorige Säure | Chlorite | |||
| +5 | Chlorsäure | Chlorate | |||
| +7 | Perchlorsäure | Perchlorate | |||
| Brom | −1 | Bromwasserstoffsäure | Bromide | ||
| +1 | Hypobromige Säure | Hypobromite | |||
| +3 | Bromige Säure | Bromite | |||
| +5 | Bromsäure | Bromate | |||
| +7 | Perbromsäure | Perbromate | |||
| Iod | −1 | Iodwasserstoffsäure | Iodide | Wässrige Lösung von Iodwasserstoff | |
| +1 | Hypoiodige Säure | Hypoiodite | |||
| +3 | Iodige Säure | Iodite | |||
| +5 | Iodsäure | Iodate | |||
| +7 | Periodsäure | (Metaperiodsäure), (Orthoperiodsäure), (Triperiodsäure) | Periodate | Es gibt verschiedenartige Periodate, weil es mehrere Periodsäuren gibt. |
Säuren der Chalkogene
| Element | Oxidationszustand | Trivialname | Formel | Salze | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schwefel | −2 | Schwefelwasserstoff | Sulfide | ||
| +2 | Sulfoxylsäure | Sulfoxylate | |||
| −1 / +5 | Thioschwefelsäure | Thiosulfate | |||
| +3 | Dithionige Säure | ||||
| +3 / +5 | Dischweflige Säure | Disulfite | |||
| +4 | Schweflige Säure | Sulfite | Entsteht durch Reaktion von Schwefeldioxid mit Wasser | ||
| +5 | Dithionsäure | Dithionate | |||
| +6 | Schwefelsäure | Sulfate | Wird mithilfe von Schwefeltrioxid hergestellt | ||
| +6 | Dischwefelsäure | Disulfate | |||
| +6 | Peroxomonoschwefelsäure | Peroxomonosulfate | |||
| +6 | Peroxodischwefelsäure | Peroxodisulfate | |||
| Selen | −2 | Selenwasserstoff | Selenide | ||
| +4 | Selenige Säure | Selenite | |||
| +6 | Selensäure | Selenate | |||
| Tellur | -2 | Tellurwasserstoff | Telluride | ||
| +4 | Tellurige Säure | Tellurite | |||
| +6 | Tellursäure | Tellurate |
Säuren der Stickstoffgruppe
| Element | Oxidationszustand | Trivialname | Formel | Salze | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stickstoff | −2 / −3 / −4 | Stickstoffwasserstoffsäure | Azide | Wird mithilfe von Hydrazin hergestellt | |
| +1 | Hyposalpetrige Säure | Hyponitrite | |||
| +3 | Salpetrige Säure | Nitrite | Wird mithilfe von Stickstoffdioxid hergestellt | ||
| +5 | Salpetersäure | Nitrate | |||
| +5 | Peroxosalpetersäure | Peroxonitrate | |||
| Phosphor | +1 | Phosphinsäure | Phosphinate | ||
| +3 | Phosphonsäure Phosphorigsäure | Phosphonate Phosphite | |||
| +5 | Hypodiphosphonsäure | Hypodiphosphonate | |||
| +5 | Diphosphonsäure | Diphosphonate | |||
| +5 | Phosphorsäure | Phosphate | Wird mithilfe von Phosphorpentoxid hergestellt | ||
| +4 | Hypodiphosphorsäure | Hypodiphosphate | |||
| +5 | Diphosphorsäure | Diphosphate | |||
| +5 | Peroxophosphorsäure | Peroxophosphate | |||
| +5 | Peroxodiphosphorsäure | Peroxodiphosphate | |||
| Arsen | +3 | Arsenige Säure | Arsenite | ||
| +5 | Arsensäure | Arsenate | |||
| Antimon | +3 | Antimonige Säure | Antimonite | ||
| +5 | Antimonsäure | Antimonate |
Säuren der Kohlenstoff- und Bor-Gruppe
| Element | Oxidationszustand | Trivialname | Formel | Salze | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kohlenstoff | +4 | Kohlensäure | Carbonate | Entsteht durch Reaktion von Kohlenstoffdioxid mit Wasser | |
| Silicium | +4 | Metakieselsäure | Metasilicate | ||
| +4 | Orthokieselsäure | Orthosilicate | |||
| +4 | Orthodikieselsäure | Orthodisilicate | |||
| Bor | +3 | Borsäure | Borate |
Säuren der Übergangsmetalle
| Element | Oxidationszustand | Trivialname | Formel | Salze |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gold | +4 | Tetrachlorogoldsäure | Tetrachloroaurate | |
| Iridium | +4 | Hexachloroiridiumsäure | Hexachloroiridate | |
| Platin | +4 | Hexachloroplatinsäure | Hexachloroplatinate | |
| +4 | Platinsäure | Platinate | ||
| Osmium | +4 | Hexachloroosmiumsäure | Hexachloroosmate | |
| Titan | +4 | Hexafluorotitansäure | Hexafluorotitanate | |
| Zirconium | +4 | Hexafluorozirconiumsäure | Hexafluorozirconate | |
| Vanadium | +5 | Vanadiumsäure | Vanadate | |
| Chrom | +6 | Chromsäure | Chromate | |
| +6 | Dichromsäure | Dichromate | ||
| Molybdän | +6 | Molybdänsäure | Molybdate | |
| Wolfram | +6 | Wolframsäure | Wolframate | |
| Mangan | +6 | Mangansäure | Manganate | |
| +7 | Permangansäure | Permanganate | ||
| Rhenium | +7 | Perrheniumsäure | Perrhenate | |
| Technetium | +7 | Pertechnetiumsäure | Pertechnetate |
Sonstige Säuren
| Trivialname | Formel | Salze |
|---|---|---|
| Amidosulfonsäure | H2N-SO2-OH | Amidosulfonate |
| Cyanwasserstoff | HCN | Cyanide |
| Cyansäure | HOCN | Cyanate |
| Fulminsäure / Knallsäure | HCNO | Fulminate |
| Isocyansäure | HNCO | Cyanate |
| Isofulminsäure / Isoknallsäure | HONC | Fulminate |
| Königswasser | Mischung aus 3 Teilen Salzsäure und 1 Teil Salpetersäure |
Organische Säuren (Auswahl)
Kurzkettige aliphatische Carbonsäuren und Derivate
| Ausgangsalkan | gesättigte Carbonsäure | ungesättigte Carbonsäuren | gesättigte Dicarbonsäuren | ungesättigte Dicarbonsäuren | Sauerstoffhaltige Derivate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methan (CH4) | Ameisensäure HCOOH | – | – | – | – |
| Ethan (C2H6) | Essigsäure H3C-COOH | – | Oxalsäure HOOC-COOH | – | Glycolsäure HOCH2-COOH Glyoxalsäure O=CH-COOH |
| Propan (C3H8) | Propionsäure H3C-CH2-COOH | Acrylsäure H2C=CH-COOH | Malonsäure HOOC-CH2-COOH | – | Milchsäure H3C-CH(OH)-COOH Tartronsäure HOOC-CH(OH)-COOH |
| n-Butan (C4H10) | Buttersäure H3C-(CH2)2-COOH | Crotonsäure H3C-CH=CH-COOH (cis-Stellung) Isocrotonsäure H3C-CH=CH-COOH (trans-Stellung) Vinylessigsäure H2C=CH-CH2-COOH | Bernsteinsäure HOOC-(CH2)2-COOH | Maleinsäure HOOC-CH=CH-COOH (cis-Stellung) Fumarsäure HOOC-CH=CH-COOH (trans-Stellung) | Gamma-Hydroxybuttersäure HO-(CH2)3-COOH Äpfelsäure HOOC-CH(OH)-CH2-COOH Weinsäure HOOC-CH(OH)-CH(OH)-COOH Oxalessigsäure HOOC-CH2-CO-COOH Quadratsäure C4H2O4 |
| n-Pentan (C5H12) | Valeriansäure H3C-(CH2)3-COOH | Allylessigsäure H2C=CH-(CH2)2-COOH | Glutarsäure HOOC-(CH2)3-COOH | – | α-Ketoglutarsäure HOOC-CH2-CH2-CO-COOH Zitronensäure HOOC-CH2-C(OH)(COOH)-CH2-COOH Isocitronensäure HOOC-CH(OH)-CH(COOH)-CH2-COOH Aconitsäure HOOC-CH=CH(COOH)-CH2-COOH |
| n-Hexan (C6H14) | Capronsäure H3C-(CH2)4-COOH | Sorbinsäure H3C-CH=CH-CH=CH-COOH (trans-Stellung) | Adipinsäure HOOC-(CH2)4-COOH | – | Gluconsäure HO-CH2-(CH(OH))4-COOH |
| n-Heptan (C7H16) | Önanthsäure H3C-(CH2)5-COOH | – | Pimelinsäure HOOC-(CH2)5-COOH | – | – |
| n-Octan (C8H18) | Caprylsäure H3C-(CH2)6-COOH | – | Suberinsäure HOOC-(CH2)6-COOH | – | – |
| n-Nonan (C9H20) | Pelargonsäure H3C-(CH2)7-COOH | – | Azelainsäure HOOC-(CH2)7-COOH | – | – |
| n-Decan (C10H22) | Caprinsäure H3C-(CH2)8-COOH | – | Sebacinsäure HOOC-(CH2)8-COOH | – | – |
Langkettige aliphatische Carbonsäuren und Derivate
Weitere Carbonsäuren und Derivate
Aminosäuren
- Hier sind nur Aminosäuren mit einem sauren Charakter angegeben.
| Trivialname (IUPAC-Name) | Formel | Salze |
|---|---|---|
| Asparaginsäure | HOOC-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH | Aspartate |
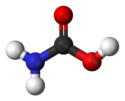
| Carbamidsäure | H2N-COOH | Carbamate |
| Glutaminsäure | HOOC-CH2-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH | Glutamate |
Weitere Carbonsäurederivate
- Hier sind weitere Derivate der Carbonsäuren angegeben, welche Fremdatome wie Halogene, Schwefel oder Phosphor enthalten.
| Trivialname (IUPAC-Name) | Formel | Salze |
|---|---|---|
| Chloressigsäure | CH2Cl-COOH | Monochloracetate |
| Fluoressigsäure | CH2F-COOH | Monofluoracetate |
| Trichloressigsäure | Cl3C-COOH | Trichloracetate |
| Trifluoressigsäure | F3C-COOH | Trifluoracetate |
Alphabetische Liste von Trivialnamen (Auswahl)
- Anmerkung: Sehr lange IUPAC-Namen sind hier teilweise weggelassen worden. Sie können im Artikel zur jeweiligen Säure nachgelesen werden.
| Trivialname | IUPAC-Name | Stäbchenmodell | Strukturformel | Formel | Charakteristische Elemente | Säurekonstanten (pKs) | Salze | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abietinsäure | Abieta-7,14-dien-19-carbonsäure |  |  | C20H30O2 | Kohlenstoff | Abietate | Bestandteil von Baumharz | |
| Acetylsalicylsäure | 2-(Acetyloxy)benzoesäure | 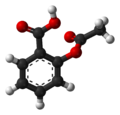 | 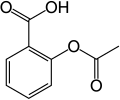 | HOOC-C6H4-COOCH3 | Kohlenstoff | 3,49 | Acetylsalicylate | Der medizinische Wirkstoff Aspirin. Ein Derivat der Salicylsäure und der Benzoesäure. |
| Acrylsäure | Propensäure |  |  | H2C=CH-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,26 | Acrylate | Eine einfach ungesättigte Carbonsäure |
| Adipinsäure | Hexandisäure |  | HOOC-(CH2)4-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,43; 5,42 | Adipate | Eine Dicarbonsäure | |
| Äpfelsäure | 2-Hydroxybutandisäure |  | 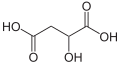 | HOOC-CH2-CH(OH)-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 3,46; 5,10 | Malate | Eine Dicarbonsäure |
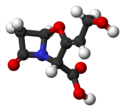
| Alendronsäure | 4-Amino-1-hydroxybutyliden -Diphosphonsäure | 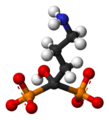 |  | C4H13NO7P2 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff, Phosphor | 2,72 | Alendronate | |
| Ameisensäure | Methansäure |  |  | HCOOH | Kohlenstoff | 3,77 | Formiate | Die einfachsteCarbonsäure und Alkansäure |
| Amidosulfonsäure | Amidoschwefelsäure |   | H2N-SO2-OH | Stickstoff, Schwefel | 1,0 | Amidosulfonate | Kommt beiStandardbedingungen nur als Zwitterion+H3N-SO3− vor | |
| Antimonige Säure | H3SbO3 | Antimon | Antimonite | |||||
| Antimonsäure | Hexahydroxoantimon(V)-säure | 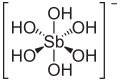 | H[Sb(OH)6] | Antimon | 2,55 | Antimonate | ||
| Arachidonsäure | 5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraensäure |  |  | C20H32O2 | Kohlenstoff | 4,752 | ||
| Arachinsäure | Eicosansäure | H3C-(CH2)18-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Arachinoate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | |||
| Arsenige Säure | Trihydrogenarsenit |  |  | H3AsO3 | Arsen | Arsenite | ||
| Arsensäure | Trihydrogenarsenat |  |  | H3AsO4 | Arsen | 2,26; 6,76; 11,29 | Arsenate | |
| Ascorbinsäure | (5R)-5-[(1S)-1,2-Dihydroxyethyl]- 3,4-dihydroxy-5-hydrofuran-2-on |  |  | C6H8O6 | Kohlenstoff | 4,25 | Ascorbate | Wird auch Vitamin C genannt |
| Barbitursäure | 2,4,6-Trihydroxy-pyrimidin |  |  | C4H4N2O3 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | 4,01 | Barbiturate | Ein Derivat des Harnstoffs |
| Behensäure | Docosansäure | H3C-(CH2)20-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Behenate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | |||
| Benzoesäure | Benzolcarbonsäure |  |  | C6H5COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,2 | Benzoate | Ein Derivat von Benzol |
| Bernsteinsäure | Butandisäure |  |  | HOOC-(CH2)2-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,16; 5,61 | Succinate | Eine Dicarbonsäure |
| Blausäure | Cyanwasserstoff |  | HCN | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | 9,40 | Cyanide | ||
| Bicinchoninsäure | 2,2'-Bichinolin-4,4'-dicarbonsäure |  | C20H12N2O4 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | Eine Dicarbonsäure | |||
| Borsäure | Trihydrogenborat | 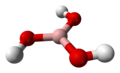 | 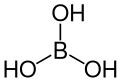 | H3BO3 | Bor | 9,24; 12,4; 13,3 | Borate | |
| Brenztraubensäure | 2-Oxopropansäure |  |  | CH3-CO-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 2,49 | Pyruvate | Die einfachste Ketosäure |
| Bromige Säure | Hydrogenbromit |  | 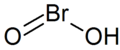 | HBrO2 | Brom | Bromite | ||
| Bromsäure | Hydrogenbromat | 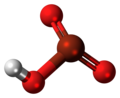 |  | HBrO3 | Brom | −2,0 | Bromate | |
| Bromwasserstoffsäure | Hydrogenbromid |  | HBr(aq) | Brom | −9,0 | Bromide | Wässrige Lösung von Bromwasserstoff. Eine Supersäure. | |
| Buttersäure | Butansäure |  |  | H3C-(CH2)2-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,82 | Butyrate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure |
| Caprinsäure | Decansäure | H3C-(CH2)8-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,9 | Decanoate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | ||
| Capronsäure | Hexansäure | H3C-(CH2)4-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,85 | Hexanoate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | ||
| Caprylsäure | Octansäure | H3C-(CH2)6-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,89 | Caprate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | ||
| Carbaminsäure | Aminomethansäure |  | 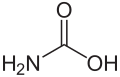 | H2N-COOH | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | Carbamate | Eine Aminosäure | |
| Cerotinsäure | Hexacosansäure |  | C25H51COOH | Kohlenstoff | Hexacosanoate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | ||
| Chinasäure | 1,3,4,5-Tetrahydroxy-cyclohexan-1-carbonsäure | 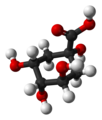 |  | C6H7(OH)4COOH | Kohlenstoff | |||
| Chloressigsäure | Monochlorethansäure |  |  | H2ClC-COOH | Kohlenstoff, Chlor | 2,87 | Monochloracetate | |
| Chlorige Säure | Hydrogenchlorit |  | HClO2 | Chlor | 1,97 | Chlorite | ||
| Chlorsäure | Hydrogenchlorat |  |  | HClO3 | Chlor | −2,7 | Chlorate | |
| Chorisminsäure | (3R)-trans-(1-Carboxyvinyloxy) -4-hydroxy-1,5-cyclohexadien-1-carbonsäure |  | C10H10O6 | Kohlenstoff | Chorismate | |||
| Chromsäure | Dihydrogenchromat | 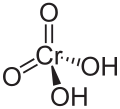 | H2CrO4 | Chrom | −0,8; 1,6 | Chromate | ||
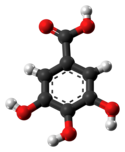
| Citronensäure | 3-Carboxy-3-hydroxy-pentan-1,5-disäure |  |  | HOOC-CH2-C(OH)(COOH)-CH2-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 3,13; 4,76; 6,4 | Citrate | Eine Tricarbonsäure |
| Clavulansäure | – |  |  | C8H9NO5 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | Clavulanate | ||
| Cyansäure | Hydrogencyanat |  |  | HOCN | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | Cyanate | ||
| Dichromsäure | Dihydrogendichromat |  | H2Cr2O7 | Chrom | Dichromate | |||
| Diphosphonsäure | Hydrogendiphosphonat | H4P2O5 | Phosphor | Diphosphonate | ||||
| Diphosphorsäure | Hydrogendiphosphate | 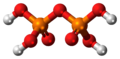 |  | H4P2O7 | Phosphor | 1,52; 2,36; 6,60; 9,25 | Diphosphate | |
| Dischwefelsäure | Dihydrogendisulfat |  |  | H2S2O7 | Schwefel | Disulfate | ||
| Ellagsäure | – | 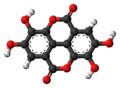 |  | C14H6O8 | Kohlenstoff | |||
| Erucasäure | cis-13-Docosensäure | H3C-(CH2)7-CH=CH-(CH2)11-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Eine einfach ungesättigte Fettsäure | ||||
| Essigsäure | Ethansäure |  |  | CH3COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,76 | Acetate | Eine Alkansäure |
| Fluoressigsäure | Monofluorethansäure |  |  | CH2F-COOH | Kohlenstoff, Fluor | 2,59 | Monofluoracetate | |
| Fluorsulfonsäure |  |  | HSO3F | Schwefel, Fluor | −10,0 | Eine Supersäure | ||
| Flusssäure | Fluorwasserstoffsäure/Hydrogenfluorid |  | HF(aq) | Fluor | 3,17 | Fluoride | Wässrige Lösung von Fluorwasserstoff | |
| Fumarsäure | (2E)-But-2-endisäure | 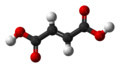 |  | HOOC-CH=CH-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 3,02; 4,38 | Fumarate | Eine einfach ungesättigte Dicarbonsäure |
| Fusarinsäure | 5-Butyl-pyridin-2-carbonsäure |  |  | C10H13NO2 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | |||
| Fusidinsäure | – |  | C31H48O6 | Kohlenstoff | Fusidate | |||
| Gallussäure | 3,4,5-Trihydroxybenzoesäure |  |  | C7H6O5 | Kohlenstoff | Gallate | ||
| Gamma-Aminobuttersäure | 4-Aminobutansäure | 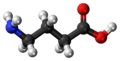 | H2N-(CH2)3-COOH | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | 4,05 | Eine Aminosäure | ||
| Gamma-Hydroxybuttersäure | 4-Hydroxybutansäure |  | HO-(CH2)3-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4-Hydroxybutyrate | |||
| Gondosäure | Eicos-11-ensäure |  | H3C-(CH2)7-CH=CH-(CH2)9-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Eine einfach ungesättigte Fettsäure | |||
| Glucarsäure | (2S,3S,4S,5R)-2,3,4,5-Tetrahydroxyhexan-1,6-disäure |  | C6H10O8 | Kohlenstoff | Glucarate | Eine Dicarbonsäure | ||
| Gluconsäure | 2,3,4,5,6-Pentahydroxyhexansäure | 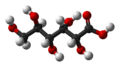 | C6H12O7 | Kohlenstoff | Gluconate | |||
| Glutarsäure | Pentandisäure | 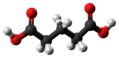 | HOOC-(CH2)3-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,32; 5,42 | Glutarate | Eine Dicarbonsäure | |
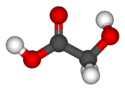
| Glycolsäure | Hydroxyethansäure |  |  | HOCH2-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 3,83 | Glycolate | |
| Glyoxalsäure | Ethanalsäure |  |  | O=CH-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 3,18; 3,32 | Glyoxylate | |
| Harnsäure | 2,6,8-Trihydroxypurin |  | 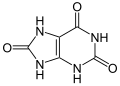 | C5H4N4O3 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | 5,75 | Urate | |
| Hexachloroiridiumsäure | Dihydrogenhexachloriridat | H2[IrCl6] | Iridium, Chlor | Hexachloroiridate | ||||
| Hexachloroosmiumsäure | Dihydrogenhexachlorosmat | H2[OsCl6] | Iridium, Chlor | Hexachloroosmate | ||||
| Hexachloroplatinsäure | Dihydrogenhexachlorplatinat | H2[PtCl6] | Platin, Chlor | Hexachloroplatinate | ||||
| Hexafluorantimonsäure | H[SbF6] | Antimon, Fluor | ||||||
| Hexafluorotitansäure | Dihydrogenhexafluorotitanat |  | H2[TiF6] | Titan, Fluor | Hexafluorotitanate | |||
| Hexafluorozirconiumsäure | Dihydrogenhexafluorozirconat | H2[ZrF6] | Zirconium, Fluor | Hexafluorozirconate | ||||
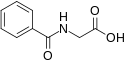
| Hippursäure | – |  | C9H9NO3 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | ||||
| Hypochlorige Säure | Hydrogenhypochlorit |  |  | HClO | Chlor | 7,54 | Hypochlorite | |
| Hypodiphosphonsäure | Tetrahydrogenhypodiphosphonat | H4P2O4 | Phosphor | Hypodiphosphonate | ||||
| Hypodiphosphorsäure | Tetrahydrogenhypodiphosphat | H4P2O6 | Phosphor | Hypodiphosphate | ||||
| Hyposalpetrige Säure | Dihydrogenhyponitrit | H2N2O2 | Stickstoff | 7,21; 11,54 | Hyponitrite | |||
| Ibotensäure | α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-isoxazolessigsäure |  | 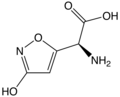 | C5H6N2O4 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | Ein Pilzgift, das unter anderem im Fliegenpilz enthalten ist | ||
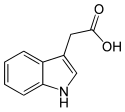
| Indol-3-essigsäure | 1H-Indol-3-Ethansäure |  |  | C10H9NO2 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | 4,75 | ||
| Iodsäure | Hydrogeniodat | 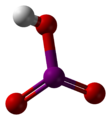 |  | HIO3 | Iod | 0,804 | Iodate | |
| Iodwasserstoffsäure | Hydrogeniodid | HI(aq) | Iod | −10,0 | Iodide | Wässrige Lösung von Iodwasserstoff. Eine Supersäure. | ||
| Isocitronensäure | 3-Carboxy-2-hydroxy-pentan-1,5-disäure |  | C6H8O7 | Kohlenstoff | Isocitrate | Eine Tricarbonsäure | ||
| Isocyansäure | Hydrogenisocyanat |  | HNCO | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | 3,92 | Cyanate | ||
| Isophthalsäure | 1,3-Benzoldicarbonsäure |  | 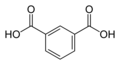 | C8H6O4 | Kohlenstoff | 3,62; 4,60 | Isophtalate | Eine Dicarbonsäure |
| α-Ketoglutarsäure | 2-Oxopentandisäure |  |  | C5H6O5 | Kohlenstoff | α-Ketoglutarate | Eine Dicarbonsäure und Ketosäure | |
| Kieselsäure | H4SiO4 | Silicium | Silicate | Es gibt mehrere Kieselsäuren. | ||||
| Knallsäure | Oxidoazaniumylidynemethan | HCNO | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | Fulminate | ||||
| Königswasser | – | Mischung aus 3 Teilen Salzsäure und 1 Teil Salpetersäure | ||||||
| Kohlensäure | Dihydrogencarbonat |  | 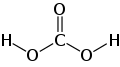 | H2CO3 | Kohlenstoff | 3,6; 10,3 | Carbonate | Entsteht durch Reaktion von Kohlenstoffdioxid mit Wasser |
| Laurinsäure | Dodecansäure | H3C-(CH2)10-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 5,3 | Laurate | |||
| Lignocerinsäure | Tetracosansäure | H3C-(CH2)22-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Lignocerate | ||||
| α-Linolensäure | (all-cis)-Octadeca-9,12,15-triensäure | 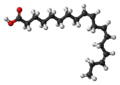 | C18H30O2 | Kohlenstoff | Eine dreifach ungesättigte Fettsäure | |||
| Linolsäure | (cis,cis)-Octadeca-9,12-diensäure | C18H32O2 | Kohlenstoff | 4,77 | Linoleate | |||
| Magische Säure | – | Mischung aus Fluorsulfonsäure und Antimon(V)-fluorid | ||||||
| Maleinsäure | (2Z)-But-2-endisäure |  |  | HOOC-CH=CH-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 1,9; 6,5 | Maleate | Eine einfach ungesättigte Dicarbonsäure |
| Malonsäure | Propandisäure |  | HOOC-CH2-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 2,83; 5,69 | Malonate | Eine Dicarbonsäure, die in Zuckerrüben enthalten ist | |
| Mandelsäure | 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylethansäure |  |  | C8H8O3 | Kohlenstoff | 3,37 | ||
| Mangansäure | Hydrogenmanganat | H2MnO4 | Mangan | Manganate | ||||
| Margarinsäure | Heptadecansäure | H3C-(CH2)15-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Heptadecanoate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | |||
| Melissinsäure | Triacontansäure | C29H59COOH | Kohlenstoff | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | ||||
| Metakieselsäure | – | H2SiO3 | Silicium | Metasilicate | Eine von mehreren Kieselsäuren | |||
| Methansulfonsäure | – |  |  | CH3S-O3H | Kohlenstoff, Schwefel | −1,9 | Mesilate | |
| Milchsäure | 2-Hydroxypropansäure |  | 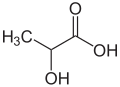 | H3C-CH(OH)-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 3,90 | Lactate | Bildet wegen ihrer optischen Aktivität die Entantiomere L-Milchsäure und D-Milchsäure |
| Molybdänsäure | Dihydrogenmolybdat | 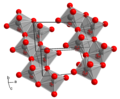 | H2MoO4 | Molybdän | 3,7; 3,9 | Molybdate | ||
| Montansäure | Octacosansäure | C27H55COOH | Kohlenstoff | Montanoate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | |||
| Myristinsäure | Tetradecansäure | H3C-(CH2)12-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Myristate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | |||
| N-Acetylneuraminsäure | – |  | C10H19NO9 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | ||||
| Nervonsäure | Delta-15-cis-Tetracosensäure | H3C-(CH2)7-CH=CH-(CH2)13-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Eine einfach ungesättigte Fettsäure | ||||
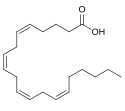
| Ölsäure | (9Z)-Octadec-9-ensäure | H3C-(CH2)7-CH=CH-(CH2)7-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Oleate | Eine einfach ungesättigte Fettsäure | |||
| Önanthsäure | Heptansäure | H3C-(CH2)5-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,89 | Heptanoate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | ||
| Orthodikieselsäure | Hexahydrogendisilicat |  | H6Si2O7 | Silicium | Orthodisilicate | Eine von mehreren Kieselsäuren | ||
| Orthokieselsäure | Tetrahydrogensilicat | H4SiO4 | Silicium | Orthosilicate | Eine von mehreren Kieselsäuren | |||
| Oxalessigsäure | 2-Oxo-butandisäure |  |  | HOOC-CH2-CO-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Oxalacetate | Eine Dicarbonsäure | |
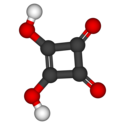
| Oxalsäure | Ethandisäure | 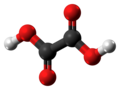 | 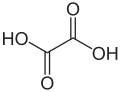 | HOOC-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 1,23; 4,19 | Oxalate | Die einfachsteDicarbonsäure |
| Palmitinsäure | Hexadecansäure | H3C-(CH2)14-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,75 | Palmitate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | ||
| Palmitoleinsäure | (9Z)-Hexadece-9-nsäure | H3C-(CH2)5-CH=CH-(CH2)7-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Eine einfach ungesättigte Fettsäure | ||||
| Pelargonsäure | Nonansäure | H3C-(CH2)7-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,96 | Pelargonate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | ||
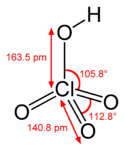
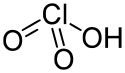
| Perchlorsäure | Hydrogenperchlorat | 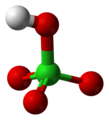 |  | HClO4 | Chlor | −10,0 | Perchlorate | Eine Supersäure |
| Permangansäure | Dihydrogenpermanganat | H2MnO4 | Mangan | Permanganate | ||||
| Peroxodischwefelsäure | Dihydrogendipersulfat |  | H2S2O8 | Schwefel | Peroxodisulfate | |||
| Peroxodiphosphorsäure | Tetrahydrogenperoxodiphosphat | H4P2O8 | Phosphor | Peroxodiphosphate | ||||
| Peroxophosphorsäure | Trihydrogenperoxophosphat | H3PO5 | Phosphor | Peroxophosphate | ||||
| Peroxosalpetersäure | Hydrogenpernitrat | 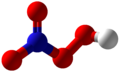 |  | HNO4 | Stickstoff | Pernitrate | ||
| Perrheniumsäure | Hydrogenperrhenat |  |  | HReO4 | Rhenium | −1,25 | Perrhenate | |
| Pertechnetiumsäure | Hydrogenpertechnetat | 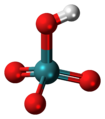 | HTcO4 | Technetium | Pertechnetate | |||
| Perxenonsäure | Tetrahydrogenperxenat |  | H4XeO6 | Xenon | Perxenate | Enthält das Edelgas Xenon | ||
| Phenylessigsäure | 1-Benzolethansäure | 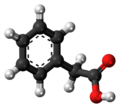 |  | C8H8O2 | Kohlenstoff | 4,28 | ||
| Phosphinsäure | Trihydrogenphosphinat |  |  | H3PO2 | Phosphor | 2,0; 2,23 | Phosphinate | |
| Phosphonsäure | Trihydrogenphosphonat | 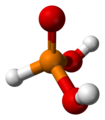 |  | H3PO3 | Phosphor | 2,0; 6,59 | Phosphonate | |
| Phosphorsäure | Trihydrogenphosphat |  |  | H3PO4 | Phosphor | 2,16; 7,21; 12,32 | Phosphate | Wird mithilfe von Phosphorpentoxid hergestellt |
| Phthalsäure | 1,2-Benzoldicarbonsäure |  |  | C8H6O4 | Kohlenstoff | 2,95; 5,41 | Phthalate | Eine Dicarbonsäure |
| Pikrinsäure | 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol | 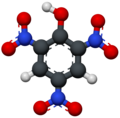 |  | C6H3N3O7 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | 0,29 | Pikrate | |
| Pimelinsäure | Heptandisäure | 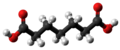 | C7H12O4 | Kohlenstoff | 4,47; 5,52 | Pimelate | ||
| Platinsäure | Dihydrogenhexahydroxoplatinat(VI) | H2Pt(OH)6 | Platin | Platinate | ||||
| Propionsäure | Propansäure |  | 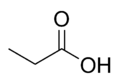 | H3C-CH2-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,87 | Propionate | Eine Alkansäure |
| Quadratsäure | 3,4-Dihydroxycyclobut-3-en-1,2-dion |  | 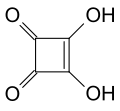 | C4H2O4 | Kohlenstoff | 1,5; 3,4 | Quadratate | Ein Derivat des Cyclobutens. Eine organische Säure ohne Carboxygruppe. |
| Ricinolsäure | 12-Hydroxy-(9Z)-octadec-9-ensäure | 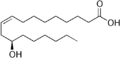 | C18H34O3 | Kohlenstoff | ||||
| Salicylsäure | 2-Hydroxybenzoesäure | 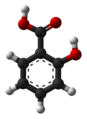 |  | C7H6O3 | Kohlenstoff | 2,75; 12,38 | Salicylate | Ist der Benzoesäure sehr ähnlich |
| Salpetersäure | Hydrogennitrat |  | HNO3 | Stickstoff | −1,37 | Nitrate | Bei dieser Verbindung tritt Mesomerie auf. | |
| Salpetrige Säure | Hydrogennitrit |  | 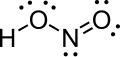 | HNO2 | Stickstoff | 3,29 | Nitrite | Wird mithilfe von Stickstoffdioxid hergestellt |
| Salzsäure | Chlorwasserstoffsäure/Hydrogenchlorid |  | HCl(aq) | Chlor | −5,9 | Chloride | Wässrige Lösung von Chlorwasserstoff. Eine Supersäure. | |
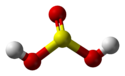
| Schwefelsäure | Dihydrogensulfat |  |  | H2SO4 | Schwefel | −3,0; 1,9 | Sulfate | Wird mithilfe von Schwefeltrioxid hergestellt |
| Schwefelwasserstoff | Dihydrogensulfid |  |  | H2S | Schwefel | 7,00; 12,92 | Sulfide | |
| Schweflige Säure | Dihydrogensulfit |  |  | H2SO3 | Schwefel | 1,81; 6,99 | Sulfite | Entsteht durch Reaktion von Schwefeldioxid mit Wasser |
| Shikimisäure | 3,4,5-Trihydroxy-1-cyclohexencarbonsäure |  |  | C7H10O5 | Kohlenstoff | 4,15 | Shikimate | |
| Sorbinsäure | (2E,4E)-2,4-Hexadiensäure | 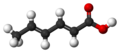 | C6H8O2 | Kohlenstoff | 4,76 | Sorbate | Eine zweifach ungesättigte Carbonsäure | |
| Stearinsäure | Octadecansäure | H3C-(CH2)16-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Stearate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | |||
| Stickstoffwasserstoffsäure | Hydrogenazid | 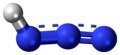 | HN3 | Stickstoff | 4,6; 7,9 | Azide | Wird mithilfe von Hydrazin hergestellt. Bei dieser Verbindung tritt Mesomerie auf. | |
| Styphninsäure | 2,4,6-Trinitro-1,3-hydroxybenzol |  |  | C6H3N3O8 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | Styphnate | Eine organische Säure ohne Carboxygruppe | |
| Sulfanilsäure | 4-Amino-1-benzolsulfonsäure | 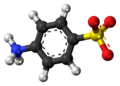 |  | C6H7NO3S | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | 3,23 | Eine organische Säure ohne Carboxygruppe | |
| Tellursäure | Hexahydrogentellurat | 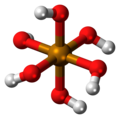 |  | H6TeO6 | Tellur | 7,70; 10,95 | Tellurate | |
| Terephthalsäure | Benzol-1,4-dicarbonsäure |  | C8H6O4 | Stickstoff | 3,54; 4,46 | Terephtalate | Eine Dicarbonsäure | |
| Tetrachlorogoldsäure | Hydrogentetrachloroaurat |  | H[AuCl4] | Gold, Chlor | Tetrachloroaurate | |||
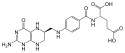
| Tetrahydrofolsäure | N-[(6S)-5,6,7,8-Tetrahydropteroyl] -L-glutaminsäure | 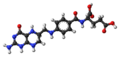 | 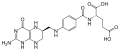 | C19H23N7O6 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | 3,51 | Eine Dicarbonsäure | |
| Thioschwefelsäure | Dihydrogenthiosulfat |  |  | H2S2O3 | Schwefel | 0,6; 1,74 | Thiosulfate | |
| Trichloressigsäure | Trichlorethansäure |  |  | Cl3C-COOH | Kohlenstoff, Chlor | 0,65 | Trichloracetate | |
| Trifluormethansulfonsäure |  |  | CF3SO3H | Kohlenstoff, Schwefel, Fluor | −20,0 | Triflate | Eine der stärksten Supersäuren | |
| Trifluoressigsäure | Trifluorethansäure | 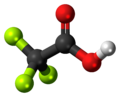 |  | F3C-COOH | Kohlenstoff, Fluor | 0,23 | Trifluoracetate | |
| Trikieselsäure | (HO)3Si–O–Si(OH)2–O–Si(OH)3. | Silicium | Trisilicate | Eine von mehreren Kieselsäuren | ||||
| Valeriansäure | Pentansäure |  |  | H3C-(CH2)3-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,84 | Valerate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure |
| Vanadiumsäure | Hydrogenvanadat | H3VO4 | Vanadium | Vanadate | ||||
| Vulpinsäure | – | 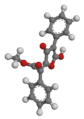 |  | C19H14O5 | Kohlenstoff | Ein Giftstoff, der in einigen Flechten enthalten ist | ||
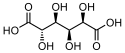
| Weinsäure | 2,3-Dihydroxybutandisäure |  | 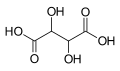 | HOOC-CH(OH)-CH(OH)-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 2,98; 4,34 | Tartrate | Eine Dicarbonsäure |
| Wolframsäure | Dihydrogenwolfrat |  | H2WO4 | Wolfram | 3,5; 4,6 | Wolframate | ||
| Xenonsäure | Dihydrogenxenat |  |  | H2XeO4 | Xenon | 10,5 | Xenate | Enthält das Edelgas Xenon |
| Zimtsäure | 3-Phenylpropensäure |  | 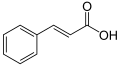 | C9H8O2 | Kohlenstoff | 4,44 |
Siehe auch
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
Struktur von Hexafluoridotitansäure
Strukturformel der Glycolsäure
Ball-and-stick model of the montanic acid molecule (also known as octacosanoic acid), a saturated fatty acid with 28 carbon atoms.
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (talk), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the pertechnetic acid molecule, a rare oxoacid of technetium.
Colour code:
- Hydrogen, H: white
- Oxygen, O: red
- Technetium, Tc: teal
Struktur von Ameisensäure
Ball-and-stick model of the acrylic acid molecule, C3H4O2.
X-ray crystallographic data from Acta Cryst. (1999). C55, IUC9900006.
Model constructed in CrystalMaker 8.1.
Image generated in Accelrys DS Visualizer.Autor/Urheber: Jynto (more from this user), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the oxalic acid molecule, the simplest dicarboxylic acid.
Atom positions based on a crystallographic study of oxalic acid dihydrate (see source).
Color code:Carbon, C: black
Hydrogen, H: white
Oxygen, O: red
Autor/Urheber: Jacopo Werther, Lizenz: CC0
Vulpinic acid - 3D - Ball-and-stick Model
- Black: Carbon, C
- White: Hydrogen, H
- Red: Oxygen, O
The structure of a Carbonic acid moe
created with bkchem+inkscape
Struktur von Isocyansäure
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (talk), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the phthalic acid molecule, an aromatic dicarboxylic acid.
Color code:
- Carbon, C: black
- Hydrogen, H: white
- Oxygen, O: red
Chemical structure of nitrous acid with electron pairs.
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (more from this user), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the pyrosulfuric acid molecule, also known as disulfuric acid, a major component of fuming sulfuric acid.
Color code:Hydrogen, H: white
Oxygen, O: red
Sulfur, S: yellow
Structural formula of the chemical compound gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB, 4-hydroxybutanoic acid, C4H8O3)
Struktur von Oxalsäure
Ball-and-stick-model of glycolic acid (2-hydroxyacetic acid). Created using Accelrys DS Visualizer Pro 1.6 and GIMP.
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (more from this user), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the glutaric acid molecule, a dicarboxylic acid.
Atom positions based on a crystallographic study of glutaric acid and urea crystallised in a 1:1 ratio (see source).
Color code:Carbon, C: black
Hydrogen, H: white
Oxygen, O: red
Autor/Urheber: PishT, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 4.0
Styphnic acid Ball and Stick
Ball-and-stick model of the lauric acid molecule, C12H24O2, AKA dodecanoic acid.
Hydrobromic acid
Autor/Urheber: PishT, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 4.0
Hyponitrous acid 1 Ball and Stick
Ball-and-stick model of the quinic acid molecule
Skeletal formula of the terephthalic acid molecule, a commodity chemical, used mainly to make polyesters.
Struktur von Zitronensäure
Struktur von gamma-Aminobuttersäure (GABA)
Ball-and-stick model of the formic acid molecule, HCO2H, molecular formula CH2O2.
Structure, determined by microwave spectroscopy, from CRC Handbook, 88th edition.
Image generated in Accelrys DS Visualizer.Autor/Urheber: Jynto (more from this user), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the malonic acid molecule, also known as propanedioic acid, a dicarboxylic acid.
Atom positions based on crystallographic data (see source).
Color code:Carbon, C: black
Hydrogen, H: white
Oxygen, O: red
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (more from this user), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the adipic acid molecule, also known as hexanedioic acid, a dicarboxylic acid with 6 carbons.
Atom positions based on a crystallographic study of urea and adipic acid crystallised in a 2:1 ratio (see source).
Color code:Carbon, C: black
Hydrogen, H: white
Oxygen, O: red
Ball-and-stick model of the boric acid molecule
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (talk), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the mandelic acid molecule, a useful precursor to various drugs. This image shows the (R)-isomer.
Color code:
- Carbon, C: black
- Hydrogen, H: white
- Oxygen, O: red
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (talk), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the trifluoroacetic acid molecule, one of the strongest carboxylic acids, at almost 100,000 times stronger than acetic acid.
Colour code:
- Carbon, C: black
- Hydrogen, H: white
- Oxygen, O: red
- Yellow-green: Fluorine, F
Struktur von Milchsäure
chemical structure of Alpha-ketoglutaric_acid
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (talk), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the fulminic acid molecule, an unstable compound which is one of the simplest to contain the four basic elements.
Colour code:
- Carbon, C: black
- Hydrogen, H: white
- Oxygen, O: red
- Nitrogen, N: blue
Chemical structure of pentanoic acid.
Struktur von Cerotinsäure (Hexacosansäure)
Molecular geometry of perchloric acid, HClO4, determined by electron diffraction in the gas phase. Based on Norman N. Greenwood, Alan Earnshaw (1997) Chemistry of the Elements (2nd Aufl.), Butterworth-Heinemann, S. 866−867 ISBN: 978-0-08-037941-8.
Ball-and-stick model of the acetic acid molecule, C2H4O2.
Structural information (determined by gas-phase electron diffraction) from CRC Handbook, 88th edition.
Image generated in Accelrys DS Visualizer.Ball-and-stick model of the sorbic acid molecule, a natural carboxylic acid used as a preservative.
Struktur von Bernsteinsäure
Struktur des Tetrachloridoaurat-Ions
Chemical structure of caprylic acid, aka octanoic acid.
Xenic acid stacture
2D-skeletal drawing of ibotenic acid
Isocitric acid.
chemical structure of 11Z-eicosenoic acid
Ball-and-stick model of the fumaric acid molecule
Chemische Strukturformel
Ball and stick model of the caprylic acid molecule (also known as octanoic acid), a saturated fatty acid found in a number of animal oils and fats, including goat milk fat.
Ball-and-stick model of the myristic acid molecule (also known as tetradecanoic acid), a saturated fatty acid with 14 carbon atoms.
Ball-and-stick model of the L-ascorbic acid (vitamin C) molecule, C6H8O6, as found in the crystal structure.
X-ray diffraction data from J. Mol. Struct.: THEOCHEM (1997) 419, 139-154.
Model constructed in CrystalMaker 8.1.
Image generated in Accelrys DS Visualizer.Oxaloacetic acid molecule model
Strukturformel von Methansulfonsäure
Chemical structure of butyric acid (butanoic acid).
Struktur von Behensäure (Docosansäure)
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (talk), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the arsenic acid molecule, an inorganic acid similar to phosphoric acid, where phosphorus is replaced by arsenic.
Colour code:
- Hydrogen, H: white
- Oxygen, O: red
- Arsenic, As: lilac
Trichloressigsäure; Trichlorethansäure; 2,2,2-Trichlorethansäure; TCA
2D structure of gallic acid
Chemical structure of lauric acid.
Autor/Urheber: Giorgiogp2, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
Ibotenic acid 3d structure
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (more from this user), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the succinic acid molecule, a dicarboxylic acid.
Atom positions based on a crystallographic study of urea and succinic acid crystallised in a 1:1 ratio (see source).
Color code:Carbon, C: black
Hydrogen, H: white
Oxygen, O: red
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (talk), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the tetrahydrofolic acid molecule, a derivative of folic acid.
Colour code:
- Carbon, C: black
- Hydrogen, H: white
- Oxygen, O: red
- Nitrogen, N: blue
chemical structure of ricinoleic acid
Chlorsäure
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (talk), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the terephthalic acid molecule, a dicarboxylic acid very widely used as an ingredient in plastic bottles.
Color code:
- Carbon, C: black
- Hydrogen, H: white
- Oxygen, O: red
Struktur von Dischwefelsäure
Ball and stick model of the caproic acid molecule (also known as hexanoic acid), a saturated fatty acid found in a number of animal oils and fats, including goat milk fat.
Ball-and-stick model of the stearic acid molecule (also known as octadecanoic acid), a saturated fatty acid with 18 carbon atoms.
Autor/Urheber: Jynto, Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the hydrogen azide molecule, also known as hydrazoic acid.
Colour code:
- Hydrogen, H: white
- Nitrogen, N: blue
Ball-and-stick model of the maleic acid molecule, structure as determined by x-ray crystallography. Structure reported in Chem. Commun. (2006) 54–56 (MALIAC12).
Resonance description of the bonding in the nitric acid molecule
Ball-and-stick model of the trans isomer of the nitrous acid molecule, HONO or HNO2. Structure calculated in Spartan using the HF/3-21G basis set.
Mandelic acid
chemical structure of Glyoxylic acid
Chemical structure of arsenous acid
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (more from this user), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the fusaric acid molecule, an antibiotic.
Color code:Carbon, C: black
Hydrogen, H: white
Nitrogen, N: blue
Oxygen, O: red
Struktur von Brenztraubensäure
Abietic acid - Made with arguslab
Skeletal formula of tetrahydrofolic acid. Created using ACD/ChemSketch 10.0 and Inkscape.
Ball-and-stick model of the dihydroxysuccinic acid molecule, tartaric acid. Made from File:DMSA-3D-balls.png, simply by pasting the blue channel of the image into the green channel.
Autor/Urheber: Andif1, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 4.0
Crystal structure of H2MnO4. Created using Diamond 4. Data from Böschen & Krebs, Kristallstruktur der 'weissen Molybdänsäure' alpha-MoO3.H20 Acta Cryst. B30 (1970), pp.1795–1800.
Chemical structure of alpha-linolenic acid showing differing numbering conventions, created with ChemDraw.
Structural formula of Hypochlorous acid
Bromsäure
Skeletal formula of clavulanic acid. Created using ACD/ChemSketch 12.0 and Inkscape. Optimized with vim.
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (talk), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the GABA molecule, also known as gamma-aminobutyric acid, one of the most important neurotransmitters in the central nervous system. This image shows the electrically neutral form.
Color code:
- Carbon, C: black
- Hydrogen, H: white
- Oxygen, O: red
- Nitrogen, N: blue
Struktur von Zimtsäure
Chemical structure of chorismic acid
Autor/Urheber: Cabcrewch, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
Sulfamic acid in zwitterion form
Struktur von Thioschwefelsäure
Structure and dimensions of the hydrogen azide molecule, HN3.
Structural data from Greenwood, N. N.; Earnshaw, A. (1997) Chemistry of the Elements (2. Aufl.), Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann ISBN: 0-7506-3365-4.Chemical structure of heptadecanoic acid
Struktur von Arachinsäure (Eicosansäure)
Ball-and-stick model of the fluoroacetic acid molecule, C2H3FO2, as found in the crystal structure
X-ray crystallographic data from: Cryst. Struct. Commun. (1978) 7, 313
Available in the CSD as entry FACETC10.
Model constructed in CrystalMaker 8.1.
Image generated in Accelrys DS Visualizer.Structure of quinic acid
Melissic acid; triacontoic acid
Sulfaminsäure-Zwitterion-Bildung
Autor/Urheber: Adam Rędzikowski, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
Model cząsteczki kwasu α-ketoglutarowego.
model build with BALLview 1.4 www.ballview.org
3D ball-and-stick of isocyanic acid made in Accelrys DS Visualizer.
Ball-and-stick model of the lignoceric acid molecule (also known as tetracosanoic acid), a saturated fatty acid with 24 carbon atoms.
Struktur von Chromsäure
Struktur von Cyansäure
- Hyponitrous acid (trans); Hyponitrite (trans)(en)
- Hyposalpetrige Säure (trans) (de)
Chemical structure of pelargonic acid, aka nonanoic acid.
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (talk), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the ellagic acid molecule, a natural antioxidant found in fruits and vegetables.
Colour code:
- Carbon, C: black
- Hydrogen, H: white
- Oxygen, O: red
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (talk), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the isophthalic acid molecule, an aromatic dicarboxylic acid used in plastics manufacture.
Color code:
- Carbon, C: black
- Hydrogen, H: white
- Oxygen, O: red
Struktur von Harnsäure (Ketoform)
Ball-and-stick model of the glyoxylic acid molecule, a compound with both aldehyde and carboxylic acid groups.
Strukturformel von Cyanwasserstoff
Chemical structure of adipic acid
Autor/Urheber: LHcheM, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
Structure of bicinchoninic acid
Struktur von Caprinsäure (Decansäure)
Struktur der Bromigen Säure
Ball-and-stick model of the nitric acid molecule, HNO3. Structural data obtained by microwave spectroscopy from A. Peter Cox and José M. Riveros (1965). "Microwave Spectrum and Structure of Nitric Acid". Journal of Chemical Physics 42: 3106-3112. DOI:10.1063/1.1696387.
Autor/Urheber: PishT, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 4.0
Peroxynitric acid Ball and Stick
Struktur von Pikrinsäure
Strukturformel von Borsäure
Struktur von Glutarsäure
Struktur von D-Gluconsäure
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (talk), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the lactic acid molecule, a compound that plays an important role in respiration, and is most commonly associated with heavy exercise. This image shows the more common (in living organisms) L-isomer.
Color code:
- Carbon, C: black
- Hydrogen, H: white
- Oxygen, O: red
chemical structure of stearic acid
Ball-and-stick model of the palmitelaidic acid molecule, the trans isomer of palmitoleic acid and a trans fat found in hydrogenated vegetable oils.
Struktur von Chloressigsäure
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (more from this user), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the pimelic acid molecule, a dicarboxylic acid with 7 carbons.
Atom positions based on a crystallographic study of pimelic acid and urea crystal (see source).
Color code:Carbon, C: black
Hydrogen, H: white
Oxygen, O: red
Struktur von Montansäure (Octacosansäure)
Ball-and-stick model of the aspirin molecule, as found in the solid state.
Single-crystal X-ray diffraction data from Kim, Y.; Machida, K.; Taga, T.; Osaki, K. (1985). "Structure Redetermination and Packing Analysis of Aspirin Crystal". Chem. Pharm. Bull. 33 (7): 2641-2647. ISSN 1347-5223.Autor/Urheber: Tpa2067, Mikayé, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
ions in solution of hydrochloric acid
Struktur von Äpfelsäure
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (talk), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the bromous acid molecule, an oxoacid of bromine in an oxidation state of +3.
Color code:
- Hydrogen, H: white
- Oxygen, O: red
- Bromine, Br: red-brown
Arsensäure; Arsen(V)-säure
Struktur von Malonsäure
Alendronsäure; Alendronat
Chemical structure of heptanoic acid created with ChemDraw. Own work.
Strukturformel von Vulpinsäure
Ball-and-stick model of the palmitic acid molecule (also known as hexadecanoic acid), a saturated fatty acid with 16 carbon atoms.
Ball-and-stick model of the hydrogen sulfide molecule, H2S
Ball-and-stick model of the Margaric acid molecule (also known as Heptadecanoic acid), a saturated fatty acid with 17 carbon atoms.
Chemical structure of fusidic acid.
Autor/Urheber: PishT, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 4.0
Hyponitrous acid 2 Ball and Stick
Autor/Urheber: Manuel Almagro Rivas, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 4.0
3D model of a picric acid molecule.
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (talk), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the α-Linolenic acid molecule, an unsaturated fatty acid.
Colour code:
- Carbon, C: black
- Hydrogen, H: white
- Oxygen, O: red
Ellagsäure
Chemical structure of peroxynitric acid
Ball and stick model of the decanoic acid molecule (also known as capric acid), a saturated fatty acid that occurs in coconut oil and in palm kernel oil, as well as the millk of various mammals.
Valeric acid molecule model
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (talk), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the bromic acid molecule, an oxoacid of bromine in an oxidation state of +5.
Color code:
- Hydrogen, H: white
- Oxygen, O: red
- Bromine, Br: red-brown
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (talk), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the indole-3-acetic_acid molecule, a plant hormone of the auxin family.
Colour code:
- Carbon, C: black
- Hydrogen, H: white
- Oxygen, O: red
- Nitrogen, N: blue
Struktur von Peroxodiphosphorsäure
Tellursäure; Orthotellursäure
Struktur von Benzoesäure
Ball-and-stick model of butyric acid (butanoic acid)
Struktur von Maleinsäure
Struktur von Lignocerinsäure (Tetracosansäure)
Struktur von Sorbinsäure
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (talk), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the Arsenous acid molecule, an inorganic acid somewhat similar to phosphorous acid, where phosphorus is replaced by arsenic.
Colour code:
- Hydrogen, H: white
- Oxygen, O: red
- Arsenic, As: lilac
Ball-and-stick model of the heptanoic acid molecule, a saturated fatty acid (also known as enanthic acid).
Autor/Urheber: Edward the Confessor, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 4.0
SVG version of Arachidonic acid.png
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (more from this user), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the phenylacetic acid molecule, a carboxylic acid found predominantly in fruits.
Color code:Carbon, C: black
Hydrogen, H: white
Oxygen, O: red
Chemical structure of Pimelic acid created with ChemDraw.
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (talk), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the telluric acid molecule, a weak inorganic acid.
Colour code:
- Hydrogen, H: white
- Oxygen, O: red
- Orange-brown: Tellurium, Te
Chemical structure of hippuric acid
Struktur des Hexahydroxidoantimonat(V)-Ions
Ball-and-stick model of the GHB molecule.
Structure calculated in Spartan '04 Student Edition. Image generated in Accelrys DS Visualizer.Ball-and-stick model of the fluorosulfuric acid molecule, one of the strongest commercially available acids, with an acid dissociation constant of approximately 10,000,000,000 (compared to 1000 for sulfuric acid).
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (more from this user), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the sulfanilic acid molecule, a standard compound in combustion analysis. This image shows it as a zwitterion.
Color code:Carbon, C: black
Hydrogen, H: white
Oxygen, O: red
Nitrogen, N: blue
Sulfur, S: yellow
Chemical structure of erucic acid.
Chemical Structure of Oxaloacetic acid.
Ball-rod model of a molecule of xenic acid.
Trifluoressigsäure; Trifluorethansäure; 2,2,2-Trifluorethansäure; TFA
Ball-and-stick model of the salicylic acid molecule, C7H6O3, from the crystal structure.
Crystal structure by X-ray diffraction from Acta Cryst. (2006). B62, 612-626.
Model constructed in CrystalMaker 8.1.
Image generated in Accelrys DS Visualizer.Autor/Urheber: Jynto (more from this user), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the gallic acid molecule, an organic acid found in many natural products, including gallnuts.
Based on the crystal structure of gallic acid monohydrate, as determined by scientific study.
Color code:Carbon, C: black
Hydrogen, H: white
Oxygen, O: red
Autor/Urheber: AbcdKolya, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
Трехмерная модель молекулы мочевой кислоты
Struktur von Dichromsäure
Strukturformel von Peroxodischwefelsäure
chemical structure of 2-phenylacetic acid created with ChemDraw
Ball-and-stick model of the linoleic acid molecule, C18H32O2, as found in the crystal structure.
X-ray diffraction data from Z. Naturforsch., B (1979) 34, 706-711.
Model constructed in CrystalMaker 8.1.
Image generated in Accelrys DS Visualizer.Ball-and-stick model of propionic acid (propanoic acid)
Ball-and-stick model of the cis isomer of the nitrous acid molecule, HONO or HNO2. Structure calculated in Spartan using the HF/3-21G basis set.
Chemical structure of caproic acid.
Autor/Urheber: Glycoform, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 4.0
N-acetyl neuraminic acid, Neu5Ac
Ball-and-stick model of the sulfuric acid molecule H2SO4.
Ball-and-stick model of the phosphonic acid molecule, H3PO3, one of two tautomers of phosphorous acid.
Structure calculated using HF/6-31G* in Spartan '04 Student Edition. Image generated in Accelrys DS Visualizer.Strukturformel von Trifluormethansulfonsäure.
Struktur von Phosphinsäure (Hypophosphorige Säure)
Chemical structure of myristic acid.
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (talk), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the pyrophosphoric acid molecule, also known as diphosphoric acid, an inorganic oxoacid.
Colour code:
- Hydrogen, H: white
- Oxygen, O: red
- Phosphorus, P: orange
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (talk), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the cyanic acid molecule, one of the simplest compounds that contains the four basic elements.
Colour code:
- Carbon, C: black
- Hydrogen, H: white
- Oxygen, O: red
- Nitrogen, N: blue
chemical structure of acrylic acid, made using BKChem
Struktur von Carbaminsäure
Autor/Urheber: Jynto (talk), Lizenz: CC0
Ball-and-stick model of the cinnamic acid molecule, a carboxylic acid found in cinnamon.
Colour code:
- Carbon, C: black
- Hydrogen, H: white
- Oxygen, O: red
Skeletal formula of fumaric acid
Malic-acid molecule model
البنية الجزيئية لحمض إندول 3-الأسيتيك