Liste der Liganden-Abkürzungen
Auf dieser Seite werden allgemein gebräuchliche Abkürzungen für Liganden in der Chemie zusammengestellt. Als Ligand wird hier allgemein eine Gruppe von Atomen oder einzelne Atomen verstanden, die an ein zentrales Teilchen koordiniert sind. Die Abkürzungen werden im Allgemeinen in die Strukturformel mit einbezogen.
Auch Aminosäuren können als Liganden koordinieren. Diese können mit dem Dreibuchstabencode bezeichnet werden.
| Abkürzung | Name | maximale Zähnigkeit (κ) | maximale Haptizität (η) | Ladung | Struktur |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetylacetonat | 2 | −1 |  | ||
| Acetonitril | 1 | 0 |  | ||
| Acetat | 1 | −1 |  | ||
| 2-(2-Aminoethylamino)ethanol | 3 | 0 |  | ||
| Wasser | 1 | 0 |  | ||
| 2,2′-bis(diphenylphosphino)-6,6′-dimethoxy-1,1′-biphenyl |  | ||||
| 2,2'-Binaphthyldiphenyldiphosphin | 2 | 0 |  | ||
| 1,2-Bis[4,5-dihydro-3H-binaphtho[1,2-c:2′,1′-e]phosphepino]benzen | |||||
| 1,1′-Bis{4,5-dihydro-3H-dinaphtho[1,2-c: 2′,1′-e]phosphepino}ferrocen | |||||
| 4,4′-Di-tert-butyl-4,4′,5,5′-tetrahydro-3,3′-bis-3H-dinaphtho[2,1-c:1′,2′-e]phosphepin | |||||
| 4,5-Dihydro-3H-dinaphtho[2,1-c;1′,2′-e]phosphepin | |||||
| 1,1′-Bi-2-naphthol | 2 | −2 |  | ||
| 5,5'-Bis-tert-butyl-bipyridin | 2 | 0 |  | ||
| 5,5'-Bis-tert-butyl-bipyridin | 2 | 0 | |||
| Benzylmethylphenylphosphin | 1 | 0 | |||
| Bis(2-((S)-4-iso-propyl-4,5-dihydrooxazol-2-yl)phenyl)amin | |||||
| Bis(2-((S)-4-tert-butyl-4,5-dihydrooxazol-2-yl)phenyl)amin | |||||
| Bis(oxazolin)-Liganden | 2 | 0 |  | ||
| 1,2-Bis(2,5-diethylphospholano)ethan | 2 | 0 | |||
| Butoxycarbonyl-4-diphenylphosphino-2-diphenylphosphinomethyl-pyrrolidin | |||||
| 2,2′-Bipyridin | 2 | 0 |  | ||
| 2,2′-Bipyridin | 2 | 0 |  | ||
| Cyclohexyl-o-anisylmethylphosphin | 1 | 0 | |||
| Bis(diphenylphosphino)butan | 2 | 0 |  | ||
| Tropylium (Cycloheptatrienyl) | 1 | 7 | +1 |  | |
| Citrat | 3 | −3 |  | ||
| 1,5-Cyclooctadien | 2 | 4 | 0 |  | |
| Cycloocten | 1 | 2 | 0 |  | |
| Cyclooctatetraen | 2 | 4 | 0 |  | |
| Cyclooctatetraen | 1 | 8 | −2 |  | |
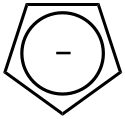
| Cyclopentadienyl | 1 | 5 | −1 |  | |
| Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl | 1 | 5 | −1 |  | |
| Diacetonalkohol | 1 | 0 |  | ||
| 1,4-Diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octan | 1 | 0 |  | ||
| Dibenzylidenaceton | 2 | 4 | 0 |  | |
| Dibenzoylmethan | 2 | −1 |  | ||
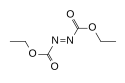
| Diethylazodicarboxylat |  | ||||
| Diethylentriamin | 3 | 0 |  | ||
| O-Isopropyliden-2,3-dihydroxy-1,4-bis(diphenylphosphino)butan | 2 | 0 |  | ||
| (1R,2R)-Bis[(2-methoxyphenyl)phenylphosphino]ethan | 2 | 0 |  | ||
| 1,2-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ethan | 2 | 0 |  | ||
| 4-Dimethylaminopyridin | 1 | 0 |  | ||
| Dimethylformamid | 1 | 0 |  | ||
| Dimethylglyoxim | 2 | −1 |  | ||
| 1,4,7,10-Tetraazacyclododecan-1,4,7,10-tetraessigsäure | 8 | −4 |  | ||
| 1,2-Bis[dimethylphosphino]ethan | 2 | 0 |  | ||
| Neocuproin (2,9-Dimethyl-1,10-phenanthrolin) | 2 | 0 |  | ||
| Dimethylsulfoxid | 1 | 0 |  | ||
| (R,R)- & (S,S)-1,2-Diphenylethylene-1,2-diamin | |||||
| 1,2-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ethan | 2 | 0 |  | ||
| Bis(diphenylphosphino)methan | 2 | 0 |  | ||
| 1,3-Bis(diphenylphosphino)propan | 2 | 0 |  | ||
| Diethylentriamin-Pentaacetat | 8 | −5 |  | ||
| Bis(2,5-dimethylphospholano)benzol | 2 | 0 | |||
| Ethylendiamintetraacetat | 6 | −4 |  | ||
| Ethylen-bis(oxyethylennitrilo)-tetraacetat | |||||
| Ethylendiamin | 2 | 0 | |||
| α,α,α′,α′-tetramethyl-1,3-benzenedipropionate (benannt nach Christine G. Espino)[1] | |||||
| Hexafluoroacetylaceton | 2 | −1 |  | ||
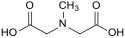
| Iminodiessigsäure | 3 | −2 | |||
| Ligand | |||||
| 2,2′-Bis[(N,N-dimethylamino)(phenyl)methyl]-1,1′-bis(dicyclohexylphosphino)ferrocen | |||||
| N | 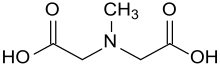 | ||||
| (3,5-Dioxa-4-phosphacyclohepta[2,1-a;3,4-a′]dinapthalen-4-yl)dimethylamin | |||||
| Methylphenyl-n-propylphosphin | |||||
| 1,3-Diketiminat | 2 | −1 | 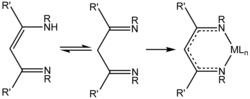 | ||
| Bicyclo[2.2.1]hepta-2,5-dienyl | 2 | 4 | 0 |  | |
| Bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-1-yl | |||||
| 2,3-Bis(diphenylphosphino)-bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en | |||||
| N-Heterocyclische Carbene |  | ||||
| Nitrilotriessigsäure | 4 | −3 |  | ||
| Acetat | 1 | −1 |  | ||
| tert-Butylat | 1 | −1 |  | ||
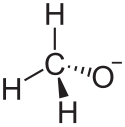
| Ethanolat | 1 | −1 | |||
| Methanolat | 1 | −1 |  | ||
| Oxalat | 2 | −2 |  | ||
| 8-Hydroxychinolin | 2 | 0 |  | ||
| Phenyl o-anisylmethylphosphin | |||||
| Tricyclohexylphosphan | 1 | 0 |  | ||
| Phthalocyanin | 4 | −2 |  | ||
| Phenanthrolin | 2 | 0 |  | ||
| Picolylamin | |||||
| Piperidin | 1 | 0 |  | ||
| Porphin |  | ||||
| Triphenylphosphan | 1 | 0 |  | ||
| 2-Phenylpyridin | 1 | 0 | |||
| Pyridyl | 1 | 0 |  | ||
| Bis(oxazolin)-Liganden | 3 | 0 |  | ||
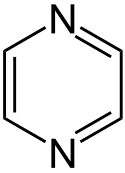
| Pyrazin | 1 | 0 |  | ||
| Quinolin-8-olato | |||||
| Bis(salicyliden)ethylendiaminat | 4 | −2 |  | ||
| Lösungsmittel (Solvent) | |||||
| 1,4,7-Triazacyclononan | |||||
| α,α,α´,α´-Tetraaryl-1,3-dioxolan-4,5-dimethanol | 2 | −2 |  | ||
| Tartrat | 4 | −2 | 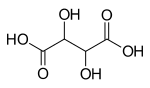 | ||
| Ethylendiaminotriacetat | 5 | −3 | |||
| Terpyridin | 3 | 0 |  | ||
| Triethylentetramin | 4 | 0 | |||
| Triflat | 1 | −1 |  | ||
| Tetramethylethylendiamin | 2 | 0 |  | ||
| Tetramethylethylendiamin | 2 | 0 |  | ||
| Tris(pyrazolyl)borat | 3 | −1 |  | ||
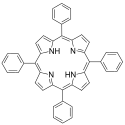
| Tetraphenylporphyrin | 4 | −2 |  | ||
| Triphenylphosphantrisulfonat | |||||
| Tris(2-aminoethyl)amin | 4 | 0 | |||
| Triethylentetramin | 4 | 0 | |||
| Triethylentetraminhexaessigsäure | 10 | −6 |  | ||
| , | Halogenid oder Pseudohalogenid |
Siehe auch
Liste der Abkürzungen in der organischen Chemie
Literatur
- Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry, IUPAC Recommendations 2005 ("Red Book"), Tabelle VII, Ligand abbreviations, S. 267. (PDF-Datei; 4,14 MB)
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ J. Du Bois et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004,126, 47, doi:10.1021/ja0446294.
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
chemical structure of a simple porphyrin ring
Wassermolekül
Struktur von TTHA
Struktur von Phthalocyanin
Autor/Urheber: Sbrools, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
Dimethylformamide. Created in Inkscape.
Struktur von Pyridin
Struktur von 8-Hydroxychinolin (8-Chinolinol)
Autor/Urheber: Tzaph, Lizenz: CC0
Struktur des Liganden dmg
Dimethylglyoxim
DimethyldioximChemical structure of cis-Cyclo-octene
Struktur des Ethanolat-Ions
Struktur des Acetat-Ions
Struktur des Calcium-NTA-Komplex-Anions (NTA:Nitrilotriessigsäure)
Struktur des Neocuproin
Struktur von Piperidin
Struktur von Diethylentriaminpentaessigsäure (DTPA)
Struktur von 1,10-Phenanthrolin
Trifluoromesylate_Anion
Strukturformeln von (R)- und (S)-BINOL.
Autor/Urheber: Project Osprey, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
Bis-oxazoline (BOX) and pyridine bis-oxazoline (PyBOX).
Structure of N1,N1'-(ethane-1,2-diyl)bis(ethane-1,2-diamine)
BINAP_Enantiomers
Strukturformel der chemischen Verbindung 2,2′-Bipyridin (Bipyridyl, Dipyridin, Dipyridyl)
Skeletal formula of the pentamethylcyclopentadienyl cation, [C5Me5]+
Struktur von Acetylaceton
Dibenzoylmethan
Autor/Urheber: Tzaph, Lizenz: CC0
Struktur des Liganden hfac Hexafluoroacetylaceton
Struktur von Bicyclo[2.2.1]hepta-2,5-dien
Terpyridin; Terpy; 2,2′:6′,2′′-Terpyridin
Tautomers of a substituted HNacNac ligand precursor and an idealised complex (right) of the conjugate base (M = metal, L = other ligand).
2-(2-Aminoethylamino)ethanol; N-(Aminoethyl)ethanolamin
Autor/Urheber: Mihafil, converted to SVG by User:Ivan A. Krestinin, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
Молекулярная структура тетрафенилпорфирина
Struktur des Methanolat-Ions
Structure of 2,2'-azanediyldiacetic acid
Die Strukturformel von DOTA = 1,4,7,10-Tetraazacyclododecan-1,4,7,10-tetraessigsäure
Struktur von Ethan-1,2-diamin
NHC general structure
Chemical diagram for tropylium ion
Struktur des Cyclopentadienyl-Anions
Autor/Urheber: BartVL71, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
Chemical structure of triphenylphosphine
TMEDA
Autor/Urheber: ChemDoc 2010, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 4.0
Strukturformel von N-Methyliminodiessigsäure
Struktur des Liganden Bis(diphenylphosphino)methan (dppm).
Struktur von 4-Hydroxy-4-methylpentan-2-on
structure of DABCO
meso-DIPAMP
Chemical structure of cyclooctatetraenide ion
dreidimensionale Gerüstformel von (all)-Z-Cyclooctatetraen (COT)
Struktur des Tris(pyrazol)borat
Struktur von Dimethylsulfoxid
Autor/Urheber: Tzaph, Lizenz: CC0
Struktur des Liganden BICHEP / MeOBIPHEP 2,2′-bis(diphenylphosphino)-6,6′-dimethoxy-1,1′-biphenyl
Struktur von
Struktur des Citrat-Ions
Chemical structure of Diethyl azodicarboxylate (DEAD)
Struktur von (S,S)-DIOP (O-Isopropyliden-2,3-dihydroxy-1,4-bis(diphenylphosphino)butan)
Chemical structure of dppp (1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane)
Structure of (1E,4E)-1,5-diphenylpenta-1,4-dien-3-one
Skeletal formula of tricyclohexylphosphine