Isidis Planitia
| Marskrater Isidis Planitia | ||
|---|---|---|
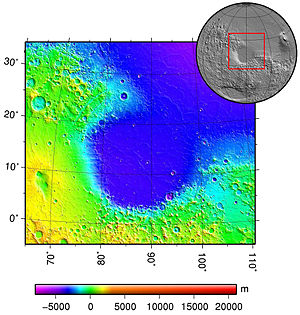 | ||
| Topografie nach MOLA, Mars Global Surveyor | ||
| Position | 14° N, 88° O | |
| Durchmesser | 1225 km | |
| Alter | etwa 3,9 Mrd. Jahre | |
Isidis Planitia ist eine kreisförmige ausgedehnte Tiefebene auf der nördlichen Hemisphäre des Planeten Mars. Sie ist nach Hellas Planitia und vor Argyre Planitia das zweitgrößte Einschlagbecken auf dem Mars. In ihrem Nordosten geht Isidis Planitia in die noch größere Tiefebene Utopia Planitia über.

Am 25. Dezember 2003 ging der Lander Beagle 2 der ESA-Sonde Mars-Express in dieser Ebene nieder (geplant: 10,6°N, 270°W); es gelang jedoch kein Funkkontakt.
Siehe auch
Weblinks
- Isidis Planitia im Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature der IAU (WGPSN) / USGS
- DLR: Die Hochlandregion Libya Montes 27. März 2006
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
Isidis basin (Mars) topography
Carte de Mars reconstituée à partir des mesures de Mars Global Surveyor (MOLA) et des observations de Viking.
Components of Beagle 2 Flight System on Mars
http://www.nasa.gov/jpl/mars/pia19106/
http://www.nasa.gov/jpl/lost-2003-mars-lander-found-by-mars-reconnaissance-orbiter/
This annotated image shows where features seen in a 2014 observation by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter have been interpreted as hardware from the Dec. 25, 2003, arrival at Mars of the United Kingdom's Beagle 2 Lander.
Beagle 2 was released by the European Space Agency's Mars Express orbiter but never heard from after its expected landing. Images from the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter have been interpreted as showing the Beagle 2 did make a soft landing and at least partially deployed its solar panels.
The 0.1-kilometer scale bar indicates a dimension of 328 feet. The location is approximately 11.5 degrees north latitude, 90.4 degrees east latitude.
The image is an excerpt from HiRISE observation ESP_037145_1915, taken June 29, 2014. Other image products from this observation are available at http://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/ESP_037145_1915 .
The University of Arizona, Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colo. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington.