IC 4597
| Galaxie IC 4597 | |
|---|---|
| AladinLite | |
| Sternbild | Skorpion |
| Position Äquinoktium: J2000.0, Epoche: J2000.0 | |
| Rektaszension | 16h 17m 39,7s[1] |
| Deklination | -34° 21′ 57″ [1] |
| Erscheinungsbild | |
| Morphologischer Typ | S / LINER [1] |
| Helligkeit (visuell) | 13,5 mag [2] |
| Helligkeit (B-Band) | 14,4 mag [2] |
| Winkelausdehnung | 1,20' × 1,0' [2] |
| Positionswinkel | 120° [2] |
| Flächenhelligkeit | 13,6 mag/arcmin² [2] |
| Physikalische Daten | |
| Rotverschiebung | 0.014487 ± 0.000024 [1] |
| Radialgeschwindigkeit | 4343 ± 7 km/s [1] |
| Hubbledistanz vrad / H0 | (192 ± 13) · 106 Lj (58,8 ± 4,1) Mpc [1] |
| Geschichte | |
| Entdeckung | Royal H. Frost |
| Entdeckungsdatum | 16. Juli 1903 |
| Katalogbezeichnungen | |
| IC 4597 • PGC 57746 • ESO 390-002 • IRAS 16144-3414 • 2MASX J16173974-3421572 • GALEXASC J161739.81-342155.5 | |
IC 4597 ist eine Linsenförmige Galaxie mit aktivem Galaxienkern vom Hubble-Typ S0/a[2] im Sternbild Skorpion am Südsternhimmel. Sie ist schätzungsweise 192 Millionen Lichtjahre von der Milchstraße entfernt und hat einen Durchmesser von etwa 65.000 Lichtjahren.
Das Objekt wurde am 16. Juli 1903 von Royal Harwood Frost entdeckt.[3]
Siehe auch
Weblinks
Einzelnachweise
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
Autor/Urheber: Torsten Bronger., Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
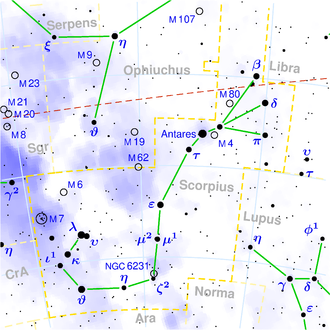
This is a celestial map of the constellation Scorpius, the Scorpion.
The yellow dashed lines are constellation boundaries, the red dashed line is the ecliptic, and the shades of blue show Milky Way areas of different brightness. The map contains all Messier objects, except for colliding ones. The underlying database contains all stars brighter than 6.5. All coordinates refer to equinox 2000.0.
The map is calculated with the equidistant azimuthal projection (the zenith being in the center of the image). The north pole is to the top. The (horizontal) lines of equal declination are drawn for 0°, ±10°, ±20° etc. The lines of equal right ascension are drawn for all 24 hours. Towards the rim there is a very slight magnification (and distortion).