HCTU
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
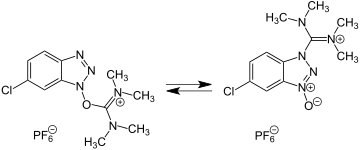 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||||||||
| Name | HCTU | ||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C11H15ClF6N5OP | ||||||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung | weißes Pulver[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 413,7 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand | fest | ||||||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | 185–190 °C[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen (0 °C, 1000 hPa). | |||||||||||||||||||
HCTU (2-(6-Chlor-1H-benzotriazol-1-yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethylaminium-hexafluorophosphat) ist ein Kopplungsreagenz, welches in der Peptidsynthese zur Erzeugung von Peptiden verwendet wird.
Die Kopplung von aktivierten Aminosäuren mit Peptiden unter Verwendung von HCTU als Hilfreagenz verläuft racemisierungsarm und innerhalb von zwei Minuten.[2][3]
Die Verbindung ist thermisch instabil und kann sich stark exotherm zersetzen. Eine DSC-Messung zeigt ab 149 °C eine Zersetzungsreaktion mit einer spezifischen Reaktionsenthalpie von −845 J·g−1 bzw. −350 kJ·mol−1.[4]
Alternative Kopplungsreagenzien sind z. B. HATU, HBTU,[5] TBTU, COMU,[6] TOMBU und COMBU.[7]
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ a b c d Datenblatt O-(6-Chlorobenzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N′,N′-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate ≥98.0% (HPLC) bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 19. Mai 2017 (PDF).
- ↑ C. A. Chantell, M. A. Onaiyekan, M. Menakuru: Fast conventional Fmoc solid-phase peptide synthesis: a comparative study of different activators. In: Journal of Peptide Science. Band 18, Nummer 2, Februar 2012, S. 88–91, doi:10.1002/psc.1419, PMID 22147296.
- ↑ Reinhard Knorr, Arnold Trzeciak, Willi Bannwarth, Dieter Gillessen: New coupling reagents in peptide chemistry. In: Tetrahedron Letters. 30, 1989, S. 1927, doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)99616-3.
- ↑ J. B. Sperry, C. J. Minteer, JingYa Tao, R. Johnson, R. Duzguner, M. Hawksworth, S. Oke, P. F. Richardson, R. Barnhart, D. R. Bill, R. A. Giusto, J. D. Weaver: Thermal Stability Assessment of Peptide Coupling Reagents Commonly Used in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing. In: Organic Process Research & Development. Band 22, 2020, S. 1262–1275, doi:10.1021/acs.oprd.8b00193.
- ↑ C. U. Hjørringgaard, A. Brust, P. F. Alewood: Evaluation of COMU as a coupling reagent for in situ neutralization Boc solid phase peptide synthesis. In: Journal of Peptide Science. Band 18, Nummer 3, März 2012, S. 199–207, doi:10.1002/psc.1438, PMID 22252935.
- ↑ R. Subirós-Funosas, L. Nieto-Rodriguez, K. J. Jensen, F. Albericio: COMU: scope and limitations of the latest innovation in peptide acyl transfer reagents. In: Journal of Peptide Science. Band 19, Nummer 7, Juli 2013, S. 408–414, doi:10.1002/psc.2517, PMID 23712932.
- ↑ Y. E. Jad, S. N. Khattab, B. G. de la Torre, T. Govender, H. G. Kruger, A. El-Faham, F. Albericio: TOMBU and COMBU as Novel Uronium-type peptide coupling reagents derived from Oxyma-B. In: Molecules. Band 19, Nummer 11, 2014, S. 18953–18965, doi:10.3390/molecules191118953, PMID 25412042.
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
Strukturformeln von Tautomeren
