GeoJSON
| GeoJSON | |
|---|---|
| Dateiendung: | .geojson |
| MIME-Type: | application/geo+json |
| Erstveröffentlichung: | Juni 2008 |
| Art: | GIS-Datenformat |
| Erweitert von: | JSON |
| Standard(s): | RFC 7946[1] |
| geojson.org | |
GeoJSON ist ein offenes Format, um geografische Daten nach der Simple-Feature-Access-Spezifikation zu repräsentieren. Dafür wird die JavaScript Object Notation verwendet.
Geschichte
Die Entwicklung des GeoJSON-Formats begann im März 2007 durch eine Gruppe von Entwicklern über eine Mailingliste.[2] Im Juni 2008 wurde die Formatspezifikation verabschiedet.
Im April 2015 gründete die Internet Engineering Task Force eine Geographic JSON working group.[3] Diese veröffentlichte GeoJSON als RFC 7946 im August 2016.[1]
Geometrien
Zu den unterstützten Geometrien zählen Punkte (beispielsweise Adressen und Point of Interest), Linien (beispielsweise Straßen und Flüsse), Polygone (beispielsweise Ländergrenzen und Landnutzungen) sowie mehrteilige Typen dieser Geometrien.
| Typ | Beispiel | |
|---|---|---|
| Point (Punkt) |  | { "type": "Point",
"coordinates": [30, 10]
}
|
| LineString (Linie) |  | { "type": "LineString",
"coordinates": [
[30, 10], [10, 30], [40, 40]
]
}
|
| Polygon |  | { "type": "Polygon",
"coordinates": [
[[30, 10], [40, 40], [20, 40], [10, 20], [30, 10]]
]
}
|
 | { "type": "Polygon",
"coordinates": [
[[35, 10], [45, 45], [15, 40], [10, 20], [35, 10]],
[[20, 30], [35, 35], [30, 20], [20, 30]]
]
}
| |
| Typ | Beispiel | |
|---|---|---|
| MultiPoint | 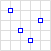 | { "type": "MultiPoint",
"coordinates": [
[10, 40], [40, 30], [20, 20], [30, 10]
]
}
|
| MultiLineString |  | { "type": "MultiLineString",
"coordinates": [
[[10, 10], [20, 20], [10, 40]],
[[40, 40], [30, 30], [40, 20], [30, 10]]
]
}
|
| MultiPolygon |  | { "type": "MultiPolygon",
"coordinates": [
[
[[30, 20], [45, 40], [10, 40], [30, 20]]
],
[
[[15, 5], [40, 10], [10, 20], [5, 10], [15, 5]]
]
]
}
|
 | { "type": "MultiPolygon",
"coordinates": [
[
[[40, 40], [20, 45], [45, 30], [40, 40]]
],
[
[[20, 35], [10, 30], [10, 10], [30, 5], [45, 20], [20, 35]],
[[30, 20], [20, 15], [20, 25], [30, 20]]
]
]
}
| |
Beispiel
{ "type": "FeatureCollection",
"features": [
{ "type": "Feature",
"geometry": {"type": "Point", "coordinates": [102.0, 0.5]},
"properties": {"prop0": "value0"}
},
{ "type": "Feature",
"geometry": {
"type": "LineString",
"coordinates": [
[102.0, 0.0], [103.0, 1.0], [104.0, 0.0], [105.0, 1.0]
]
},
"properties": {
"prop0": "value0",
"prop1": 0.0
}
},
{ "type": "Feature",
"geometry": {
"type": "Polygon",
"coordinates": [
[ [100.0, 0.0], [101.0, 0.0], [101.0, 1.0],
[100.0, 1.0], [100.0, 0.0] ]
]
},
"properties": {
"prop0": "value0",
"prop1": {"this": "that"}
}
}
]
}
Softwareunterstützung
GeoJSON wird von einer Vielzahl von freien Geoinformationssystemen und Mapping-Software unterstützt, beispielsweise OpenLayers,[4] Leaflet,[5] MapLibre GL JS,[6] MapServer,[7] GeoServer,[8] GeoDjango,[9] PointPlot,[10] GDAL,[11] QGIS,[12] und CartoDB.[13] Des Weiteren kann GeoJSON in PostGIS[14][15] und Mapnik (Standard-Renderer von OpenStreetMap)[16][17] verwendet werden, weil diese beiden Softwarepakete auf die GDAL-Bibliothek zurückgreifen.
Bing Maps, Yahoo! und Google Maps verwenden/unterstützen GeoJSON in deren Programmierschnittstellen.
GitHub zeigt GeoJSON-Dateien auf einer interaktiven Karte an.[18]
GeoJSON.io ist ein interaktiver GeoJSON-Editor in Form einer Webanwendung.[19]
Siehe auch
- Geography Markup Language (GML)
- Keyhole Markup Language (KML)
- GPS Exchange Format (GPX)
Weblinks
- geojson.org
- The GeoJSON Format Specification. geojson.org
- geojson.io – Werkzeug zum interaktiven Erstellen von GeoJSON-Dateien
- Christopher Andrews: Emerging Technology: AJAX and GeoJSON. 18. September 2007, ehemals im (nicht mehr online verfügbar); abgerufen am 26. Januar 2024 (englisch). (Seite nicht mehr abrufbar. Suche in Webarchiven)
- GeoWebGuru: Technical Overview: GeoJSON. 16. Februar 2009, archiviert vom am 12. August 2016; abgerufen am 2. Juli 2023 (englisch).
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ a b RFC – The GeoJSON Format. August 2016 (englisch).
- ↑ March 2007 Archives by thread
- ↑ Geographic JSON (geojson). In: ietf.org. Abgerufen am 12. August 2016.
- ↑ GeoJSON. In: openlayers.org. Abgerufen am 12. August 2016.
- ↑ Documentation – Leaflet – a JavaScript library for interactive maps. In: leafletjs.com. Abgerufen am 12. August 2016.
- ↑ Sources. In: maplibre.org. Abgerufen am 14. Mai 2023.
- ↑ Template-Driven Output – MapServer 7.0.1 documentation. In: mapserver.org. Abgerufen am 12. August 2016.
- ↑ OGR based WFS Output Format – GeoServer 2.10.x User Manual. In: docs.geoserver.org. Abgerufen am 12. August 2016.
- ↑ GeoJSON Serializer. In: docs.djangoproject.com. Abgerufen am 12. August 2016.
- ↑ PointPlot. In: ndm.io. Ehemals im (nicht mehr online verfügbar); abgerufen am 12. August 2016. (Seite nicht mehr abrufbar. Suche in Webarchiven)
- ↑ GeoJSON. In: gdal.org. Abgerufen am 12. August 2016.
- ↑ 14.1. Öffnen von Daten. In: QGIS Dokumentation docs.qgis.org. Abgerufen am 7. Juli 2022.
- ↑ CARTO Documentation – CARTO Documentation. In: developers.cartodb.com. Archiviert vom am 27. Juni 2014; abgerufen am 12. August 2016.
- ↑ ST_GeomFromGeoJSON. In: postgis.net. Abgerufen am 12. August 2016.
- ↑ ST_AsGeoJSON. In: postgis.net. Abgerufen am 12. August 2016.
- ↑ GeoJSON-Plugin von Mapnik auf GitHub
- ↑ osmwiki:Mapnik
- ↑ There’s a map for that. 13. Juni 2013, abgerufen am 12. August 2016.
- ↑ geojson.io
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
Autor/Urheber: Mwtoews, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
Simple feature access/well-known text to describe a MultiPolygon with a hole using
MULTIPOLYGON (((40 40, 20 45, 45 30, 40 40)),
((20 35, 10 30, 10 10, 30 5, 45 20, 20 35),
(30 20, 20 15, 20 25, 30 20))) Autor/Urheber: Mwtoews, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
Simple feature access/well-known text to describe a MultiLineString using
MULTILINESTRING ((10 10, 20 20, 10 40),
(40 40, 30 30, 40 20, 30 10)) Autor/Urheber: Mwtoews, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
Simple feature access/well-known text to describe a MultiPolygon using
MULTIPOLYGON (((30 20, 45 40, 10 40, 30 20)),
((15 5, 40 10, 10 20, 5 10, 15 5))) Autor/Urheber: Mwtoews, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
Simple feature access/well-known text to describe a MultiPoint using
MULTIPOINT ((10 40), (40 30), (20 20), (30 10)) Autor/Urheber: Mwtoews, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
Simple feature access/well-known text to describe a LineString using
LINESTRING (30 10, 10 30, 40 40) Autor/Urheber: Mwtoews, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
Simple feature access/well-known text to describe a Polygon using
POLYGON ((30 10, 40 40, 20 40, 10 20, 30 10)) Autor/Urheber: Mwtoews, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
Simple feature access/well-known text to describe a Polygon with a hole using
POLYGON ((35 10, 45 45, 15 40, 10 20, 35 10),
(20 30, 35 35, 30 20, 20 30)) Autor/Urheber: Mwtoews, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
Simple feature access/well-known text to describe a Point using
POINT (30 10) 






