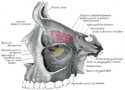
Fossa pterygopalatina
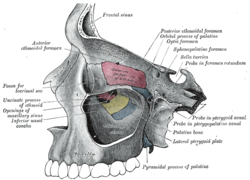


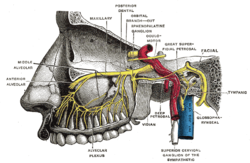
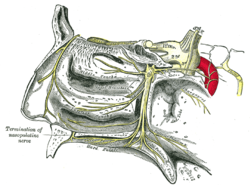

Die Fossa pterygopalatina (Flügelgaumengrube) ist eine knöchern begrenzte Grube (lat. fossa) am Schädel.
Grenzen
Sie hat folgende Grenzen:
- nach vorne (anterior): Maxilla (Facies infratemporalis)
- nach hinten (posterior) und nach oben (kranial): Os sphenoidale (Processus pterygoideus)
- zur Mitte (medial): Os palatinum (Lamina perpendicularis)
- nach unten (kaudal): Sie verengt sich zum Canalis palatinus major
- seitlich (lateral): Fissura pterygomaxillaris (Durchtritt der A. maxillaris, abgehend von Fossa infratemporalis zu Fossa pterygopalatina)
Verbindungen
Die Fossa pterygopalatina hat Verbindungen zu anderen Teilen des Schädels:
| Richtung | Verbindung | Ziel |
|---|---|---|
| nach vorne (anterior) | Fissura orbitalis inferior | Orbita |
| nach unten (inferior) | Canalis palatinus major | Mundhöhle und Canales palatini minores |
| nach außen (lateral) | Fissura pterygomaxillaris | Fossa infratemporalis |
| nach innen (medial) | Lamina perpendicularis ossis palatini und Foramen sphenopalatinum | Nasenhöhle |
| nach hinten (posterior) |
|
|
Inhalt
In der Fossa pterygopalatina liegen folgende anatomische Strukturen:
- Ganglion pterygopalatinum (mit Verbindung zum Nervus maxillaris)
- der dritte Abschnitt der Arteria maxillaris (pars pterygopalatina)
- Nerv im Canalis pterygoideus (N. petrosus major (parasympathisch) und N. petrosus profundus (sympathisch) = N. canalis pterygoideus)
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
Sphenoid bone. Anterior and inferior surfaces.
The sphenopalatine ganglion and its branches.
Alveolar branches of superior maxillary nerve and sphenopalatine ganglion. (Testut.)
Left maxillary sinus opened from the exterior.
Articulation of left palatine bone with maxilla.