c-Fos
| FOS | ||
|---|---|---|
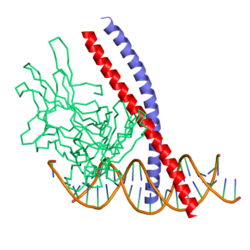 | ||
| nach PDB 1A02 | ||
| Andere Namen |
| |
| Eigenschaften des menschlichen Proteins | ||
| Masse/Länge Primärstruktur | 380 Aminosäuren, 40695 Da | |
| Bezeichner | ||
| Externe IDs | ||
| Vorkommen | ||
| Homologie-Familie | Hovergen | |
| Orthologe | ||
| Mensch | Hausmaus | |
| Entrez | 2353 | 14281 |
| UniProt | P01100 | P01101 |
| PubMed-Suche | 2353 | 14281 |
c-FOS ist ein Bestandteil des Transkriptionsfaktors AP-1 und ein Protoonkogen.[1]
Eigenschaften
Zur gleichen Fos-Proteinfamilie gehören auch FosB, Fra-1 und Fra-2 sowie die kleineren FosB Spleißvarianten FosB2 und ΔFosB.[2] Das Gen gehört zu den Immediate early genes. Das Protein c-Fos bindet an BCL3,[3] COBRA1,[4] CSNK2A1,[5] CSNK2A2,[5] DDIT3,[6] c-Jun[7][8][9][10][11][12][13] NCOA1,[14][15] NCOR2,[16] RELA,[7] RUNX1,[17][18] RUNX2,[17][18] SMAD3[19] und TBP.[20]
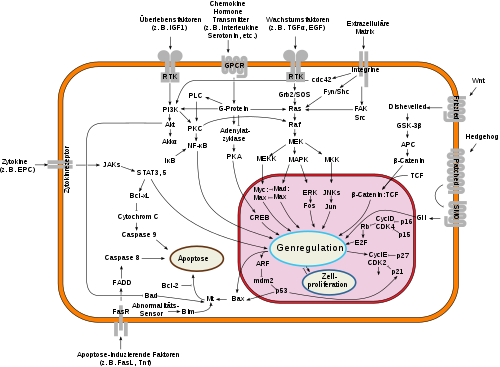 |
Mutationen im Gen von c-Fos treten bei verschiedenen Tumoren auf. Das Homolog des c-Fos aus Retroviren wird als v-Fos (virales Fos) bezeichnet.
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ Chiu R, Boyle WJ, Meek J, Smeal T, Hunter T, Karin M: The c-Fos protein interacts with c-Jun/AP-1 to stimulate transcription of AP-1 responsive genes. In: Cell. 54. Jahrgang, Nr. 4, August 1988, S. 541–52, doi:10.1016/0092-8674(88)90076-1, PMID 3135940.
- ↑ Milde-Langosch K: The Fos family of transcription factors and their role in tumourigenesis. In: European Journal of Cancer. 41. Jahrgang, Nr. 16, November 2005, S. 2449–61, doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2005.08.008, PMID 16199154.
- ↑ Na SY, Choi JE, Kim HJ, Jhun BH, Lee YC, Lee JW: Bcl3, an IkappaB protein, stimulates activating protein-1 transactivation and cellular proliferation. In: J. Biol. Chem. 274. Jahrgang, Nr. 40, Oktober 1999, S. 28491–6, doi:10.1074/jbc.274.40.28491, PMID 10497212.
- ↑ Zhong H, Zhu J, Zhang H, Ding L, Sun Y, Huang C, Ye Q: COBRA1 inhibits AP-1 transcriptional activity in transfected cells. In: Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 325. Jahrgang, Nr. 2, Dezember 2004, S. 568–73, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.10.079, PMID 15530430.
- ↑ a b Yamaguchi Y, Wada T, Suzuki F, Takagi T, Hasegawa J, Handa H: Casein kinase II interacts with the bZIP domains of several transcription factors. In: Nucleic Acids Res. 26. Jahrgang, Nr. 16, August 1998, S. 3854–61, doi:10.1093/nar/26.16.3854, PMID 9685505, PMC 147779 (freier Volltext).
- ↑ Ubeda M, Vallejo M, Habener JF: CHOP enhancement of gene transcription by interactions with Jun/Fos AP-1 complex proteins. In: Mol. Cell. Biol. 19. Jahrgang, Nr. 11, November 1999, S. 7589–99, PMID 10523647, PMC 84780 (freier Volltext).
- ↑ a b Yang X, Chen Y, Gabuzda D: ERK MAP kinase links cytokine signals to activation of latent HIV-1 infection by stimulating a cooperative interaction of AP-1 and NF-kappaB. In: J. Biol. Chem. 274. Jahrgang, Nr. 39, September 1999, S. 27981–8, doi:10.1074/jbc.274.39.27981, PMID 10488148.
- ↑ Ito T, Yamauchi M, Nishina M, Yamamichi N, Mizutani T, Ui M, Murakami M, Iba H: Identification of SWI.SNF complex subunit BAF60a as a determinant of the transactivation potential of Fos/Jun dimers. In: J. Biol. Chem. 276. Jahrgang, Nr. 4, Januar 2001, S. 2852–7, doi:10.1074/jbc.M009633200, PMID 11053448.
- ↑ Pognonec P, Boulukos KE, Aperlo C, Fujimoto M, Ariga H, Nomoto A, Kato H: Cross-family interaction between the bHLHZip USF and bZip Fra1 proteins results in down-regulation of AP1 activity. In: Oncogene. 14. Jahrgang, Nr. 17, Mai 1997, S. 2091–8, doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201046, PMID 9160889.
- ↑ Glover JN, Harrison SC: Crystal structure of the heterodimeric bZIP transcription factor c-Fos-c-Jun bound to DNA. In: Nature. 373. Jahrgang, Nr. 6511, Januar 1995, S. 257–61, doi:10.1038/373257a0, PMID 7816143.
- ↑ Nomura N, Zu YL, Maekawa T, Tabata S, Akiyama T, Ishii S: Isolation and characterization of a novel member of the gene family encoding the cAMP response element-binding protein CRE-BP1. In: J. Biol. Chem. 268. Jahrgang, Nr. 6, Februar 1993, S. 4259–66, PMID 8440710.
- ↑ Finkel T, Duc J, Fearon ER, Dang CV, Tomaselli GF: Detection and modulation in vivo of helix-loop-helix protein-protein interactions. In: J. Biol. Chem. 268. Jahrgang, Nr. 1, Januar 1993, S. 5–8, PMID 8380166.
- ↑ Venugopal R, Jaiswal AK: Nrf2 and Nrf1 in association with Jun proteins regulate antioxidant response element-mediated expression and coordinated induction of genes encoding detoxifying enzymes. In: Oncogene. 17. Jahrgang, Nr. 24, Dezember 1998, S. 3145–56, doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202237, PMID 9872330.
- ↑ Lee SK, Na SY, Jung SY, Choi JE, Jhun BH, Cheong J, Meltzer PS, Lee YC, Lee JW: Activating protein-1, nuclear factor-kappaB, and serum response factor as novel target molecules of the cancer-amplified transcription coactivator ASC-2. In: Mol. Endocrinol. 14. Jahrgang, Nr. 6, Juni 2000, S. 915–25, doi:10.1210/mend.14.6.0471, PMID 10847592.
- ↑ Lee SK, Kim HJ, Na SY, Kim TS, Choi HS, Im SY, Lee JW: Steroid receptor coactivator-1 coactivates activating protein-1-mediated transactivations through interaction with the c-Jun and c-Fos subunits. In: J. Biol. Chem. 273. Jahrgang, Nr. 27, Juli 1998, S. 16651–4, doi:10.1074/jbc.273.27.16651, PMID 9642216.
- ↑ Lee SK, Kim JH, Lee YC, Cheong J, Lee JW: Silencing mediator of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors, as a novel transcriptional corepressor molecule of activating protein-1, nuclear factor-kappaB, and serum response factor. In: J. Biol. Chem. 275. Jahrgang, Nr. 17, April 2000, S. 12470–4, doi:10.1074/jbc.275.17.12470, PMID 10777532.
- ↑ a b Hess J, Porte D, Munz C, Angel P: AP-1 and Cbfa/runt physically interact and regulate parathyroid hormone-dependent MMP13 expression in osteoblasts through a new osteoblast-specific element 2/AP-1 composite element. In: J. Biol. Chem. 276. Jahrgang, Nr. 23, Juni 2001, S. 20029–38, doi:10.1074/jbc.M010601200, PMID 11274169.
- ↑ a b D'Alonzo RC, Selvamurugan N, Karsenty G, Partridge NC: Physical interaction of the activator protein-1 factors c-Fos and c-Jun with Cbfa1 for collagenase-3 promoter activation. In: J. Biol. Chem. 277. Jahrgang, Nr. 1, Januar 2002, S. 816–22, doi:10.1074/jbc.M107082200, PMID 11641401.
- ↑ Zhang Y, Feng XH, Derynck R: Smad3 and Smad4 cooperate with c-Jun/c-Fos to mediate TGF-beta-induced transcription. In: Nature. 394. Jahrgang, Nr. 6696, August 1998, S. 909–13, doi:10.1038/29814, PMID 9732876.
- ↑ Metz R, Bannister AJ, Sutherland JA, Hagemeier C, O’Rourke EC, Cook A, Bravo R, Kouzarides T: c-Fos-induced activation of a TATA-box-containing promoter involves direct contact with TATA-box-binding protein. In: Mol. Cell. Biol. 14. Jahrgang, Nr. 9, September 1994, S. 6021–9, doi:10.1128/MCB.14.9.6021, PMID 8065335, PMC 359128 (freier Volltext).
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
Autor/Urheber: cybertory, German translation by Furfur, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 4.0
Schematische Darstellung von verschiedenen intrazellulären Signaltransduktionswegen.
Autor/Urheber: A2-33, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
DNA-binding domains from NFAT, Fos and Jun bound to DNA. From PDB entry 1A02

