Butylbenzole
Die Butylbenzole bilden in der Chemie eine Stoffgruppe von vier aromatischen Kohlenwasserstoffen mit allen vier Varianten der Butylgruppe als Substituenten am Benzol. Durch deren unterschiedliche Anordnung ergeben sich vier Konstitutionsisomere mit der Summenformel C10H14. Sie gehören auch zur Gruppe der C4-Benzole.
Vertreter
| Butylbenzole | ||||||||||||
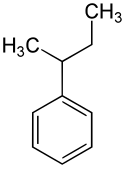
| Name | n-Butylbenzol | iso-Butylbenzol | sec-Butylbenzol | tert-Butylbenzol | ||||||||
| Andere Namen | 1-Phenylbutan | 2-Methyl-1-phenylpropan | 2-Phenylbutan | 2-Methyl-2-phenylpropan | ||||||||
| Strukturformel |  |  |  | 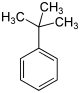 | ||||||||
| CAS-Nummer | 104-51-8 | 538-93-2 | 135-98-8 | 98-06-6 | ||||||||
| PubChem | 7705 | 10870 | 8680 | 7366 | ||||||||
| Summenformel | C10H14 | |||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 134,22 g·mol−1 | |||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand | flüssig | |||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | −88 °C[1][2] | −51 °C[3][4] | −75 °C[5] | −58 °C[6][7] | ||||||||
| Siedepunkt | 183 °C[1][2] | 173 °C[4][8] | 173 °C[5] | 169 °C[6][7] | ||||||||
| Dichte | 0,86 g·cm−3 (20 °C)[1] | 0,85 g·cm−3 (20 °C)[4] | 0,86 g·cm−3 (20 °C)[5] | 0,87 g·cm−3 (20 °C)[6] | ||||||||
| Dampfdruck (20 °C) | 1,3 hPa[1] | 1,8 hPa[4] | 1,33 hPa (19 °C)[5] | 2,2 hPa[6] | ||||||||
| Dampfdruck (30 °C) | 2,33 hPa (25 °C)[5] | 4,08 hPa[6] | ||||||||||
| Dampfdruck (50 °C) | 15 hPa[4] | 15 hPa[5] | 12,5 hPa[6] | |||||||||
| Dampfdruck (65 °C) | 20 hPa[1] | 25 hPa[4] | 30 hPa[5] | |||||||||
| Löslichkeit | 14 mg·l−1 (25 °C)[1] | 10 mg·l−1 (25 °C)[4] | 17,6 mg·l−1 (20 °C)[5] | 30 mg·l−1 (25 °C)[6] | ||||||||
| praktisch unlöslich in Wasser, löslich in organischen Lösungsmitteln | ||||||||||||
| Flammpunkt | 58 °C[1] | 48 °C[4] | 52 °C[5] | 44 °C[6] | ||||||||
| Untere Explosionsgrenze (UEG) | 0,8 Vol.-%[1] | 0,8 Vol.-%[4] | 0,8 Vol.-%[5] | 0,8 Vol.-%[6] | ||||||||
| 44 g·m−3[1] | 44 g·m−3[4] | 44 g·m−3[5] | 44 g·m−3[6] | |||||||||
| Obere Explosionsgrenze (OEG) | 5,8 Vol.-%[1] | 6,0 Vol.-%[4] | 6,9 Vol.-%[5] | 5,6 Vol.-%[6] | ||||||||
| 330 g·m−3[1] | 335 g·m−3[4] | 385 g·m−3[5] | 310 g·m−3[6] | |||||||||
| Zündtemperatur | 420 °C[1] | 425 °C[4] | 415 °C[5] | 445 °C[6] | ||||||||
| Temperaturklasse | T2 | |||||||||||
| GHS- Kennzeichnung |
|
|
|
| ||||||||
| H- und P-Sätze | 226 | 226‐410 | 226‐302‐410 | 226‐315 | ||||||||
| keine EUH-Sätze | keine EUH-Sätze | keine EUH-Sätze | keine EUH-Sätze | |||||||||
| 210‐370+378 | ? | 210‐233‐240‐273‐370+378‐403+235 | 210‐233‐240‐241‐242‐303+361+353 | |||||||||
Darstellung
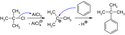
Ausgehend von Benzol gelingt unter Katalyse mit wasserfreiem Aluminiumchlorid die Darstellung von tert-Butylbenzol mit 2-Chlor-2-methylpropan (tert-Butylchlorid) als Elektrophil in einer Friedel-Crafts-Alkylierung:

Weblinks
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Eintrag zu n-Butylbenzol in der GESTIS-Stoffdatenbank des IFA, abgerufen am 28. Januar 2024. (JavaScript erforderlich)
- ↑ a b Datenblatt Butylbenzene bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 27. November 2012 (PDF).
- ↑ Datenblatt Isobutylbenzene bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 27. November 2012 (PDF).
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Eintrag zu iso-Butylbenzol in der GESTIS-Stoffdatenbank des IFA, abgerufen am 28. Januar 2024. (JavaScript erforderlich)
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Eintrag zu sec-Butylbenzol in der GESTIS-Stoffdatenbank des IFA, abgerufen am 28. Januar 2024. (JavaScript erforderlich)
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Eintrag zu tert-Butylbenzol in der GESTIS-Stoffdatenbank des IFA, abgerufen am 28. Januar 2024. (JavaScript erforderlich)
- ↑ a b Datenblatt tert-Butylbenzene bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 27. November 2012 (PDF).
- ↑ CRC Handbook of Tables for Organic Compound Identification. 3. Auflage. 1984, ISBN 0-8493-0303-6.
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) pictogram for flammable substances
iso-Butylbenzol; 1-Phenyl-2-methylpropan
Synthesis of tert-butylbenzene by Friedel-Crafts alkylation with 2-chloro-2-methylpropane
sec-Butylbenzol; 2-Phenylbutan
n-Butylbenzol; 1-Butylbenzol; 1-Phenylbutan
tert-Butylbenzol; 2-Phenyl-2-methylpropan; t-Butylbenzol
Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) pictogram for environmentally hazardous substances