Autostrada A6 (Italien)
| Autostrada 6 in Italien | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| La Verdemare Torino – Savona | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Karte | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basisdaten | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Betreiber: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Straßenbeginn: | Moncalieri (44° 57′ 56″ N, 7° 42′ 14″ O) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Straßenende: | Savona (44° 17′ 24″ N, 8° 26′ 30″ O) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gesamtlänge: | 124,0 km | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nutzungsvoraussetzung: | Mautpflicht: geschlossenes System | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ausbauzustand: | 2 × 2 und 2 × 3 Fahrstreifen | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Die Brücke Franco Romano von Fossano aus gesehen | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
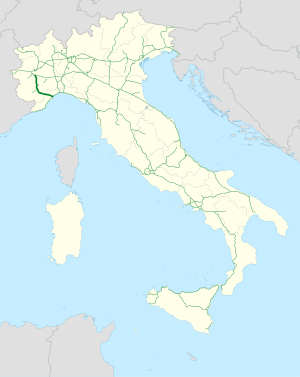
Straßenverlauf
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Die Autostrada A6 (italienisch für ‚Autobahn A6‘), auch La Verdemare (it. für ‚Autobahn des grünen Meeres‘) genannt, ist eine italienische Autobahn und führt im Nordwesten des Landes von Turin nach Savona. Sie verbindet die Hauptstadt des Piemonts mit dem Südteil der Region, vor allem die Provinz Cuneo sowie der italienischen Riviera.
Sie ist insgesamt 131 km lang, mit Ausnahme eines kurzen sechsstreifigen Abschnitts bei Turin vierstreifig und vollständig mautpflichtig.
Geschichte
Die A6 wurde bis 1971 als dreispurige Schnellstraße gebaut. Die mittlere Spur diente dabei abwechselnd in beiden Richtungen als Überholspur. 1973 begann der 4-spurige Ausbau, der 2000 abgeschlossen wurde. Im Abschnitt Ceva - Savona wurde die Autobahn dabei neu trassiert. Die alte Trasse dient heute dem Verkehr in Richtung Savona. Die Eröffnung der Abschnitte im Einzelnen:
- Ceva - Savona (heute Fahrtrichtung Savona) 27. Januar 1960
- Fossano - Ceva 28. September 1965
- La Rotta - Marene 27. Mai 1970
- Torino - La Rotta 13. August 1971
- Altare - Ceva (Fahrtrichtung Turin) 25. Mai 1976
- Savona - Altare (Fahrtrichtung Turin) 7. Oktober 1976
- Rivere - Montecalla 6. November 2000
Im Jahr 1971 wurde zwischen der Anschlussstelle Carmagnola und der Raststätte Rio Colorè-West der öffentliche Verkehr ausgeschlossen, da die Trasse von Fiat als Teststrecke für Hochgeschwindigkeitsversuche genutzt wurde.
Am 24. November 2019 stürzte bei Altare nahe Savona das Viadukt Madonna del Monte ein (siehe auch Liste von Brückeneinstürzen).[1]
Verlauf
Die A6 lässt sich in zwei Abschnitte einteilen, in den flacheren Teil der westlichen Poebene und den gebirgigen Teil hinunter nach Savona zum Mittelmeer.[2]
Turin – Cuneo (Piemont)
Die A6 beginnt südlich von Turin an der Tangenziale Sud und führt in ziemlich geraden Verlauf vorbei an Carmagnola bis östlich von Cuneo. Dabei kreuzt sie die neugebaute A33 bei Marene, die auch als Umfahrung für Turin in Richtung A21 Piacenza / Brescia genutzt werden kann, bzw. führt ein weiterer Arm der A33 in Richtung Cuneo.
Cuneo – Savona (Piemont/Ligurien)
Gleich nach der Ausfahrt Cuneo beginnt der bergige Teil der A6. Zunächst geht es bis Ceva im Tal des Tanaro parallel zur SS28. Nach Ceva teilt sich die Fahrbahn mehrere Male. Sie überschreitet den Colle di Cadibona (435 m) und damit auch die Wasserscheide zwischen dem Ligurischen Apennin und dem Po-Tal. Die Ausfahrt Millesimo ist nur von der Fahrbahn in Richtung Savona anfahrbar, so dass zwei Verbindungsstücke zur anderen Fahrbahn gebaut wurden. In zahlreichen Serpentinen geht es dann weiter hinunter nach Savona, wo die A6 auf die A10 trifft.
Regionale Bedeutung
Die A6 hat vor allem Bedeutung für den westlichen Teil des Piemonts um die Städte Cuneo, Bra, Fossano und Mondovì sowie die Zufahrt zu den Skigebieten der Meeralpen. Im überregionalen Verkehr bildet sie vor allem eine schnelle Route zwischen Turin und Genua.
Zubringer Fossano
| Autostrada 6 in Italien | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Raccordo Fossano (Zubringer Fossano) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basisdaten | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Betreiber: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Straßenbeginn: | Bene Vagienna (44° 32′ 8″ N, 7° 47′ 17″ O) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Straßenende: | Fossano (44° 32′ 29″ N, 7° 43′ 23″ O) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gesamtlänge: | 6,6 km | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nutzungsvoraussetzung: | mautfrei | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ausbauzustand: | 2 × 1 Fahrstreifen | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Straßenverlauf
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Der Zubringer von Fossano, oder Abzweig nach Fossano, weist trotz einer einzigen Fahrbahn mit jeweils einer Spur pro Fahrtrichtung die Verkehrszeichen für den Beginn und das Ende der Autobahn auf und ist grün beschildert. Darüber hinaus befinden sich am Zubringer zusätzliche Tafeln, die die Straße mit dem Symbol der Autobahn A6 kennzeichnen. Dieser Autobahnzubringer wird gemäß der internen Nummerierung von Autostrade per l’Italia auch als Zweig D06 klassifiziert.
Das Gesetzesdekret vom 29. Oktober 1999 n. 461 stufte diesen Straßenabschnitt als Autobahnzubringer der A6 ein.
Der Zubringer erstreckt sich über 6,1 km Länge ab der Anschlussstelle Fossano auf der A6.
Weblinks
- La Verdemare
- Homepage des Betreibers Autostrada dei Fiori
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ Bei Genua: Autobahnbrücke in Italien eingestürzt. In: blick.ch. 24. November 2019, abgerufen am 24. November 2019.
- ↑ Bauwerke entlang der A6 ( des vom 9. August 2020 im Internet Archive) Info: Der Archivlink wurde automatisch eingesetzt und noch nicht geprüft. Bitte prüfe Original- und Archivlink gemäß Anleitung und entferne dann diesen Hinweis.
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
(c) OOjs UI Team and other contributors, MIT
An icon from the OOjs UI MediaWiki lib.
Wellenlinie als Gewässersymbol für die Formatvorlage Autobahn
Tankstellen-Piktogramm
Zeichen 391 – Mautpflichtige Strecke, StVO 2003. Farblich korrekte Umsetzung der Originalvorlage mit dem digitalen RAL-Farbton „Verkehrsrot“. Im Verkehrsblatt, Heft 24, 1976, Seite 786, wird das Zeichen „Zollstelle“, aus dem Zeichen 391 abgeleitet wurde, in seinen Details abgebildet. Die Gesamtgröße beträgt in der Regel 600 x 600 mm, in Ausnahmefälle ist eine andere Größe möglich. Die Lichtkantenbreite beträgt 10 mm, der rote Rahmen ist 24 mm breit. Die Versalhöhe beträgt bei Zeichen 391 insgesamt 100 mm. Der Ausrundungshalbmesser am linken und rechten Ende des schwarzen Balkens beträgt 50 mm.
See below.
end of motorway symbol, coloured in green
Icon of autostrada A55 "Tangenziale Nord/Tangenziale Sud di Torino", Italy.
Autor/Urheber: Arbalete, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 4.0
Mappa dell’autostrada A6.
Icon of european road 70, Italy.
INT 1 Standardsymbol IN 10 - Empfohlener Ankerplatz (ohne definierte Grenzen)
Nach unten zeigendes schwarzes Dreieck ▼, U+25BC aus dem Unicode-Block Geometrische Formen (25A0–25FF)
Zeichen 125 – Gegenverkehr. Mit der StVO-Novelle von 1992 eingeführte neue Pfeil-Darstellungen.
Icon of state road SS28 del Colle di Nava, Italy.
Autor/Urheber: F Ceragioli, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
A6 bridge on Stura di Demonte seen from Fossano (CN, Italy)
See below.
Nach links zeigendes schwarzes Dreieck ◀, U+25C0 aus dem Unicode-Block Geometrische Formen (25A0–25FF)
This image is from a collection commissioned by the United States Department of Transportation and designed by AIGA. It is copyright-free, and is available here
Nach rechts zeigendes schwarzes Dreieck ▶, U+25B6 aus dem Unicode-Block Geometrische Formen (25A0–25FF)
Icon of autostrada A10 "Autostrada dei Fiori", Italy.
See below.
Segnale di inizio autostrada (figura II 345 dell'articolo 135 del Regolamento di attuazione del Codice della Strada).
Dimensioni: larghezza 170 cm, altezza 300 cm.
Icon of autostrada A33, Italy.
(Autobahn)tunnel (Icon). Gezeichnet nach dem Vorbild schweizerischer Verkehrsschilder.
Simbolo della strada europea 80, Italia. Per la realizzazione mi sono basato sull'immagine File:Italian traffic signs - strada europea 21.svg
Icon of autostrada A6 "La Verdemare", Italy.
Icon of european road E717 Italy.