NGC 7674
| Galaxie NGC 7674 | |
|---|---|
.](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/24/Hubble_Interacting_Galaxy_NGC_7674_%282008-04-24%29.jpg/300px-Hubble_Interacting_Galaxy_NGC_7674_%282008-04-24%29.jpg) | |
| NGC7674 (m) & “NGC 7674A” (u) mit LEDA 71507[1](Hubble-Weltraumteleskop). | |
| AladinLite | |
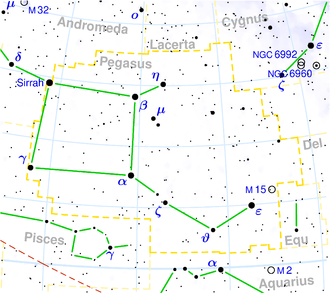
| Sternbild | Pegasus |
| Position Äquinoktium: J2000.0, Epoche: J2000.0 | |
| Rektaszension | 23h 27m 56,7s[2] |
| Deklination | +08° 46′ 45″ [2] |
| Erscheinungsbild | |
| Morphologischer Typ | SA(r)bc / pec / HII / Sy2 [2] |
| Helligkeit (visuell) | 13,1 mag [3] |
| Helligkeit (B-Band) | 13,9 mag [3] |
| Winkelausdehnung | 1,1′ × 1′ [3] |
| Positionswinkel | 150° [3] |
| Flächenhelligkeit | 13,1 mag/arcmin² [3] |
| Physikalische Daten | |
| Zugehörigkeit | HCG 96 WBL 716 |
| Rotverschiebung | 0,028924 ± 0,000030 [2] |
| Radialgeschwindigkeit | (8671 ± 9) km/s [2] |
| Hubbledistanz vrad / H0 | (394 ± 28) · 106 Lj (120,8 ± 8,5) Mpc [2] |
| Geschichte | |
| Entdeckung | John Herschel |
| Entdeckungsdatum | 16. August 1830 |
| Katalogbezeichnungen | |
| NGC 7674 • UGC 12608 • PGC 71504 • CGCG 406-112 • MCG +01-59-080 • IRAS 23254+0830 • KUG 2325+085 • 2MASX J23275670+0846443 • Arp 182 • HCG 96A • VV 343a • GC 4968 • h 2243 • GALEXASC J232756.81+084644.9 | |
NGC 7674 ist eine aktive Balken-Spiralgalaxie mit ausgedehnten Sternentstehungsgebieten vom Hubble-Typ SBbc im Sternbild Pegasus am Nordsternhimmel. Sie ist schätzungsweise 394 Millionen Lichtjahre von der Milchstraße entfernt und hat einen Durchmesser von etwa 130.000 Lichtjahren. Gemeinsam mit PGC 71505 (NGC 7674A) bildet sie das wechselwirkende Galaxienpaar Arp 182 und zusammen mit NGC 7675 und PGC 71507 das Galaxienquartett HCG 96.
Halton Arp gliederte seinen Katalog ungewöhnlicher Galaxien nach rein morphologischen Kriterien in Gruppen. Diese Galaxie gehört zu der Klasse Galaxien mit schmalen Filamenten.
Im September 2017 wurde hier ein doppeltes supermassives Schwarzes Loch mit Hilfe der Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) beobachtet. Hierbei handelt es sich um zwei einander im Abstand von 1,1 Lichtjahren umkreisende Objekte mit einer Gesamtmasse von 36 Millionen Sonnenmassen.[4]
Das Objekt wurde am 16. August 1830 von John Herschel entdeckt.[5]
Literatur
- Jeff Kanipe und Dennis Webb: The Arp Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies – A Chronicle and Observer´s Guide, Richmond 2006, ISBN 978-0-943396-76-7
Weblinks
Einzelnachweise
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
NGC 7674 (seen just above the center), also known as Markarian 533, is the brightest and largest member of the so-called Hickson 96 compact group of galaxies, consisting of four galaxies. This stunning Hubble image shows a spiral galaxy nearly face-on. The central bar-shaped structure is made up of stars. The shape of NGC 7674, including the long narrow streamers seen to the left of and below the galaxy can be accounted for by tidal interactions with its companions. NGC 7674 has a powerful active nucleus of the kind known as a type 2 Seyfert that is perhaps fed by gas drawn into the center through the interactions with the companions. NGC 7674 falls into the family of luminous infrared galaxies and is featured in Arp's Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies as number 182. It is located in the constellation of Pegasus, the Winged Horse, about 400 million light-years away from Earth.
This image is part of a large collection of 59 images of merging galaxies taken by the Hubble Space Telescope and released on the occasion of its 18th anniversary on 24th April 2008.
| About the object | |
|---|---|
| Object name | NGC 7674, Mrk 533, HCG 96, Arp 182, VV 343a |
| Object description | Interacting Galaxies |
| Position (J2000) | 23 27 56.88 +08 46 46.5 |
| Constellation | Pegasus |
| Distance | 350 million light-years (100 million parsecs) |
| About the data | |
| Data description | The Hubble image was created using HST data from proposal 10592: A. Evans (University of Virginia, Charlottesville/NRAO/Stony Brook University) |
| Instrument | ACS/WFC |
| Exposure date(s) | June 9, 2002 |
| Exposure time | 33 minutes |
| Filters | F435W (B) and F814W (I) |