Amundsensee

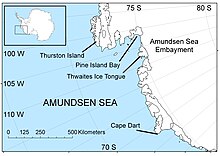

Die Amundsensee (norwegisch Amundsenhavet) ist ein Randmeer des Südpolarmeers (bzw. des Südpazifiks nach alter Lesart) und befindet sich vor der Westküste von Antarktika in Höhe des 110° westlichen Längengrades zwischen Kap Dart auf der Siple-Insel im Westen und Kap Flying Fish auf Thurston-Insel im Osten.[1] Östlich grenzt sie an die Bellingshausensee, unmittelbar westlich der Siple-Insel an den Wrigley Gulf und 1000 Kilometer weiter im Westen liegt das Rossmeer. Dazwischen liegt entlang der Hobbs-, Ruppert- und Saunders-Küste ein bislang unbenanntes Randmeer.[2]
Der norwegische Kapitän Nils Larsen, der das Meer im Februar 1929 an Bord seines Schiffs Norvegia erkundete, benannte das Meer nach dem norwegischen Polarforscher Roald Amundsen (1872–1928). Da das Meer im Allgemeinen dicht mit Packeis zugefroren ist, war der genaue Küstenverlauf bis zum Februar 1940 unbekannt, bis Teilnehmer der United States Antarctic Service Expedition (1939–1941) unter der Leitung des US-amerikanischen Polarforschers Richard Evelyn Byrd Aufklärungsflüge in der Region unternahmen. 1946 versuchten zwei Eisbrecher im Rahmen von Operation Highjump (1946–1947), das Meer zu durchqueren, um möglichst nahe an den küstennahen Schildvulkan Mount Siple heranzukommen, mussten jedoch das Vorhaben wegen der Eisverhältnisse abbrechen.[3]
In die Amundsen-See mündet der Thwaites-Gletscher. Von der Gletscherzunge brach im Jahr 2002 ein 3400 km² großer Eisberg ab. Wissenschaftler der University of Leeds ermittelten zwischen 1996 und 2021 einen Schwund von 3331 ±420 Milliarden Tonnen Eis in der Region der Amundsensee, wodurch der Meeresspiegel weltweit um etwas mehr als neun Millimeter anstieg.[4]
Siehe auch
Weblinks
- Amundsen Sea. In: Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior, archiviert vom (englisch).
- Amundsen Sea auf geographic.org (englisch)
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ Australian Antarctic Data Centre: Amundsen Sea
- ↑ Andrew Jon Hund (Hrsg.): Antarctica and the Arctic Circle: A Geographic Encyclopedia of the Earth's Polar Regions: Amundsen Sea. ABC-Clio, Santa Barbara 2014, ISBN 978-1-61069-392-9.
- ↑ William J. Mills: Exploring Polar Frontiers: A Historical Encyclopedia. ABC-Clio, Santa Barbara 2003, ISBN 1-57607-422-6, S. 20.
- ↑ Amundsensee-Region hat drei Billionen Tonnen Eis verloren. In: Spiegel Online, 21. März 2023, abgerufen am 21. März 2023.
Koordinaten: 73° 0′ 0″ S, 112° 0′ 0″ W
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
Autor/Urheber: NASA's Earth Observatory, Lizenz: CC BY 2.0
To download the full resolution and other files go to: earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=76308&src=...
Flying over Antarctica’s Pine Island Glacier in a DC-8 research plane, scientists participating in NASA’s IceBridge mission made a startling discovery on October 14: a massive crack running about 29 kilometers (18 miles) across the glacier’s floating tongue. The rift is 80 meters (260 feet) wide on average and 50 to 60 meters (165 to 195 feet) deep, and it marks the moment of creation for a new iceberg that will span about 880 square kilometers (340 square miles) once it breaks loose from the glacier.
These photographs show the rift on October 26, 2011, when scientists returned to survey the glacier in greater detail. The Digital Mapping System took the top photo, looking straight down from the belly of the DC-8. The lower photo was taken by a passenger on the jet.
Birthing large icebergs is nothing new for the Pine Island Glacier. Among the fastest moving glaciers in Antarctica, Pine Island drains about 79 cubic kilometers (19 cubic miles) of ice per year from the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. The end of the glacier stretched about 48 kilometers (30 miles) past the edge of land, floating on the ocean. As more ice flows toward the water, the tongue grows longer. Eventually, a piece will break off, forming a large iceberg.
The last calving event occurred in late 2001 and resulted in an iceberg that measured 42 kilometers by 17 kilometers (26 by 11 miles). That event, too, was preceded by a large crack that was observed in satellite imagery in late 2000.
While satellites have tracked the formation of new icebergs, this is the first detailed airborne survey of such an event. “We are actually now witnessing how it happens,” said IceBridge project scientist Michael Studinger. “It’s part of a natural process but it’s pretty exciting to be here and actually observe it while it happens.”
IceBridge scientists were surveying the Pine Island Glacier to learn how the glacier is changing and why. In the largest airborne survey of Earth’s polar ice, the airplanes of Operation IceBridge carry an array of instruments to measure the ice from top to bottom. The research team is gathering data about how thick the ice is (about 500 meters or 1,640 feet in the region of the crack); what the ground beneath it looks like; and how the glacier has changed over time. All of this information will help scientists understand why the Pine Island Glacier drains so much ice to the ocean and how much it could contribute to sea level rise in the future.
“IceBridge exists because we need to understand how much ice the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets will contribute to sea level rise over the next couple of decades,” says Studinger in a new feature article on the Earth Observatory. “In order to do this, we need to measure how much the ice surface elevation is changing from year to year.“ As a primary outlet for the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, the Pine Island Glacier is one of the largest sources of uncertainty in global sea level rise projections.
Operation IceBridge is now in the third of six annual field campaigns to Antarctica from Punta Arenas, Chile. “A lot of times when you’re in science, you don’t get a chance to catch the big stories as they happen because you’re not there at the right place at the right time,” said John Sonntag, Instrument Team Lead for Operation IceBridge. “But this time we were.”
To read more about IceBridge, see IceBridge: Buiding a record of Earth’s changing ice, one flight at a time on the Earth Observatory.
NASA images courtesy Digital Mapping System team and Michael Studinger. Caption by Holli Riebeek and Patrick Lynch.
The Earth Observatory's mission is to share with the public the images, stories, and discoveries about climate and the environment that emerge from NASA research, including its satellite missions, in-the-field research, and climate models.
Like us on Facebook
Follow us on TwitterMap of the Amundsen Sea area of Antarctica
Karte der Antarktis


