Alcedo (Vulkan)
| Alcedo | ||
|---|---|---|
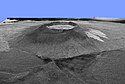
 Radarbild des Alcedo | ||
| Höhe | 1130 m | |
| Lage | Galápagos-Insel Isabela | |
| Koordinaten | 0° 25′ 29″ S, 91° 7′ 8″ W | |
| Typ | Schildvulkan | |
| Letzte Eruption | 1993 | |
Der Alcedo ist einer der kleinsten und niedrigsten von 6 Schildvulkanen auf der Galápagos-Insel Isabela. Er ist auch unter dem Namen Volcan Calderon bekannt.
Seine Höhe beträgt 1.130 Meter und sein letzter Ausbruch ereignete sich 1993 am südlichen Teil der Caldera. Der Großteil seiner Hänge und die Caldera sind bewaldet, die Nordflanke wird jedoch beherrscht von jungen Lavaströmen. Der Alcedo ist der einzige Vulkan der Galapagos-Inseln, welcher rhyolithische wie auch basaltische Lava gefördert hat. In der Caldera befindet sich ein aktives Geothermalfeld. Historische Aufzeichnungen belegen einen weiteren Ausbruch um das Jahr 1953 (± 7 Jahre) an der Südost-Flanke nahe der Cartago-Bucht.
Weblinks
- Alcedo im Global Volcanism Program der Smithsonian Institution (englisch)
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
This is a three-dimensional view of Isabela, one of the Galapagos Islands located off the western coast of Ecuador, South America. This view was constructed by overlaying a Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) image on a digital elevation map produced by TOPSAR, a prototype airborne interferometric radar which produces simultaneous image and elevation data. The vertical scale in this image is exaggerated by a factor of 1.87. The SIR-C/X-SAR image was taken on the 40th orbit of space shuttle Endeavour. The image is centered at about 0.5 degree south latitude and 91 degrees west longitude and covers an area of 75 by 60 kilometers (47 by 37 miles). The radar incidence angle at the center of the image is about 20 degrees. The western Galapagos Islands, which lie about 1,200 kilometers (750 miles) west of Ecuador in the eastern Pacific, have six active volcanoes similar to the volcanoes found in Hawaii and reflect the volcanic processes that occur where the ocean floor is created. Since the time of Charles Darwin's visit to the area in 1835, there have been more than 60 recorded eruptions on these volcanoes. This SIR-C/X-SAR image of Alcedo and Sierra Negra volcanoes shows the rougher lava flows as bright features, while ash deposits and smooth pahoehoe lava flows appear dark. Vertical exaggeration of relief is a common tool scientists use to detect relationships between structure (for example, faults, and fractures) and topography. ----- Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth. The radars illuminate Earth with microwaves allowing detailed observations at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. SIR-C/X-SAR uses three microwave wavelengths: L-band (24 cm), C-band (6 cm) and X-band (3 cm). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to better understand the global environment and how it is changing. The SIR-C/X-SAR data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity. SIR-C was developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory. X-SAR was developed by the Dornier and Alenia Spazio companies for the German space agency, Deutsche Agentur fuer Raumfahrtangelegenhe iten (DARA), and the Italian space agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI)
Autor/Urheber: Hellerick, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 4.0
Topographic and bathymetric map of the Galápagos Islands, Ecuador.