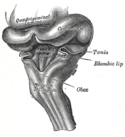
Human brainstem-thalamus posterior view description
John A Beal, PhD
Dep't. of Cellular Biology & Anatomy, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center ShreveportHuman brainstem and thalamus - posterior view
- Taenia choroidea (and lateral: Lamina affixa, Stria terminalis)
- Thalamus, Pulvinar thalami
- (Ventriculus tertius)
- Stalk of Glandula pinealis
- Habenula
- Stria medullaris
- Colliculus superior
- Brachium colliculi superioris
- Colliculus inferior
- Brachium colliculi inferioris
- Corpus geniculatum mediale
- Sulcus medianus
- Pedunculus cerebellaris superior
- Pedunculus cerebellaris inferior
- Pedunculus cerebellaris medius
- Tuberculum anterius thalami
- Obex, Area postrema
A: Thalamus, B: Mesencephalon, C: Pons, D: Medulla oblongata
On this specimen, the following thalamic structures can be seen: 1. the Epithalamus (Stria Medullaris Thalami, Habenula, & Pineal), 2. the Anterior Nucleus of the dorsal thalamus (Anterior Tubercle) and, 3. the Pulvinar (the large posterior portion of the dorsal thalamus which overhangs the midbrain.
The Medulla, Pons & Midbrain are delineated on the posterior surface of the brainstem.
NOTE: The 4 Colliculi of the tectum are refered to collectively as the Quadrigeminal Plate.
The three Cerebellar Peduncles are shown here as they enter the brainstem on each side. In the Midbrain identify the Superior Colliculus and Inferior Colliculus. Also identify the Brachium of the Superior Colliculus and the Brachium of the Inferior Colliculus which connect with the Lateral Geniculate Body and Medial Geniculate Body, respectively.
The cerebellum forms the roof of the 4th ventricle and is connected to the brainstem by 3 pairs of peduncles or pillars (shown on right side of brainstem) . The peduncles are made up of axons entering and leaving the cerebellum. The Inferior Cerebellar peduncle projects from the medulla, the large Middle Cerebellar Peduncle projects from the Pons, and the Superior Cerebellar Peduncle connects with the midbrain.
Relevante Bilder
Relevante Artikel
MittelhirnDas Mittelhirn oder Mesencephalon ist ein Teil des Hirnstamms und liegt zwischen Brücke (Pons) und Zwischenhirn (Diencephalon). Während das Mittelhirn bei Fischen und Reptilien noch übergeordnete integrative Funktionen ausübt und Sehbahn, Hörbahn und die Bahnen der Oberflächensensibilität hier enden, ist es bei Säugetieren die Verbindung zwischen Rautenhirn und Zwischenhirn und vor allem für die Koordination der Motorik zuständig, wird dabei aber durch übergeordnete Zentren weitgehend kontrolliert. Das Mittelhirn steuert die meisten Augenmuskeln und ist ein wichtiger Bestandteil des extrapyramidalen Systems. .. weiterlesen
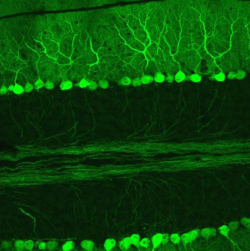
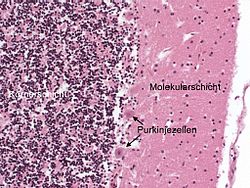
KleinhirnDas Kleinhirn oder lateinisch Cerebellum ist ein Teil des Gehirns von Wirbeltieren, der gemeinsam mit dem Brücke (Pons) genannten Bereich des Hirnstamms das Hinterhirn (Metencephalon) bildet. Hinterhirn und Markhirn bilden zusammen das Rautenhirn (Rhombencephalon). Das Kleinhirn entwickelt sich über der Rautengrube aus der Kleinhirnplatte und ist bei Wirbeltierarten verschieden stark ausgebildet. Es liegt beim Menschen unterhalb der Okzipitallappen des Großhirns in der hinteren Schädelgrube dem Hirnstamm rückenseits auf. .. weiterlesen