EverestMosaic
- The photo mosaic uses photos ISS008-E-13302 TO 13307 taken 28 January 2004 taken from the International Space Station, Expedition 8 and added to The Gateway to Astronaut Photography. From The Gateway to Astronaut Photography of Earth
"On Top of the World: Everest and Makalu:
Astronauts on board the International Space Station (ISS) have a unique view of the world because of their position in a low orbit (200 nautical miles, 360 km) relative to satellites and their ability to look at any angle out the windows of the spacecraft. ISS crewmembers recently took advantage of their vantage point to photograph a series of oblique views of the Himalayas looking south from over the Tibetan Plateau.
At first glance, one might think that the image looks like a picture taken from an airplane, until you remember that the summits of Makalu [left (8,462 meters; 27,765 feet)] and Everest [right (8,850 meters; 29,035 feet)] are at the heights typically flown by commercial aircraft. The full mosaic covers over 130 kilometers (80 miles) of the Himalayan front, and could never be seen this way from an airplane. The image is part of a larger panorama mosaic of the Himalayas that can be interactively viewed. The popular Find Mt. Everest feature is used to train astronauts to be able to find the peak in a few seconds as they pass over the Himalayas."
Relevante Bilder
Relevante Artikel
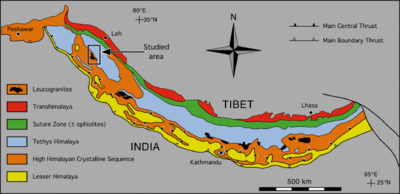
HimalayaDer Himalaya ist ein Hochgebirgssystem in Asien. Es ist das höchste Gebirge der Erde und liegt zwischen dem indischen Subkontinent im Süden und dem Tibetischen Hochland im Norden. Die Begrenzungen im Westen und Osten sind nicht geologisch begründet und werden daher unterschiedlich gezogen. Das Gebirge erstreckt sich auf einer Länge von mindestens 2500 Kilometern von Pakistan bis zum indisch-chinesischen Grenzgebiet in Arunachal Pradesh und erreicht eine Breite von bis zu 330 Kilometern. Im Himalaya befinden sich zehn der vierzehn Berge der Erde, deren Gipfel mehr als 8000 Meter hoch sind („Achttausender“), darunter der Mount Everest, der mit 8848 m ü. d. Meer höchste Berg der Erde. Mit seiner südlichen Lage sowie dem sich im Rückraum des Himalaya als ausgedehntes Hochplateau erhebenden Tibetischen Hochland übt der Himalaya großen Einfluss auf das Klima Süd- und Südostasiens aus. So wird der Indische Sommermonsun erst durch die im Sommer thermisch bedingten Ferrel'schen Druckgebilde in Westindien und Tibet erzeugt. An der Haupterhebung des Himalaya gestaut, liegen hier einige der regenreichsten Orte der Erde sowie die Quellgebiete aller großen Flusssysteme Südasiens. .. weiterlesen