Dipole xmting antenna animation 4 408x318x150ms
Relevante Bilder

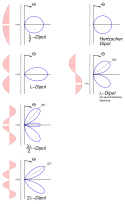



























Relevante Artikel
AntenneEine Antenne ist eine technische Anordnung zur Abstrahlung und zum Empfang elektromagnetischer Wellen, oft zur drahtlosen Kommunikation. Als Sendeantenne wandelt sie leitungsgebundene elektromagnetische Wellen in Freiraumwellen um, oder umgekehrt als Empfangsantenne die als Freiraumwelle ankommenden elektromagnetischen Wellen zurück in leitungsgebundene elektromagnetische Wellen. Wesentlich dafür ist die Transformation des Wellenwiderstandes der Leitung durch die Antennenanordnung in den Wellenwiderstand des Vakuums. Dabei entsteht eine elektromagnetische Freiraumwelle erst im Fernfeld. Anordnungen für Frequenzen unterhalb der Schumann-Resonanzen von etwa 16 Hz können aufgrund der großen Wellenlänge auf der Erde keine Freiraumwelle erzeugen. .. weiterlesen
