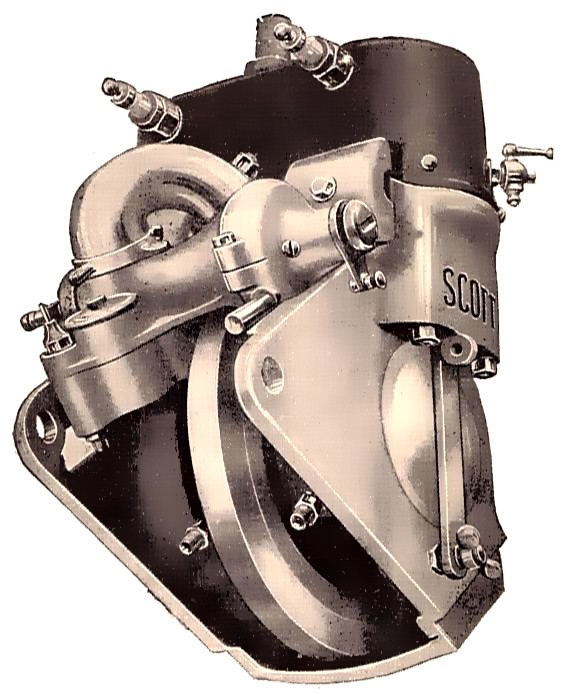
Scott two-cylinder two-stroke motorcycle engine
Fig. 198 Scott two-cylinder two-stroke motorcycle engine
Scans from 'The Book of the Motor Car', Rankin Kennedy C.E., 1912
See other images from this source in Scans from 'The Book of the Motor Car'- A photograph, which has never previously been made available to the public (e.g. by publication or display at an exhibition) and which was taken more than 70 years ago (before 1 January 1954); or
- A photograph, which was made available to the public (e.g. by publication or display at an exhibition) more than 70 years ago (before 1 January 1954); or
- An artistic work other than a photograph (e.g. a painting), or a literary work, which was made available to the public (e.g. by publication or display at an exhibition) more than 70 years ago (before 1 January 1954).
![]() This tag can be used only when the author cannot be ascertained by reasonable enquiry. If you wish to rely on it, please specify in the image description the research you have carried out to find who the author was. The above is all subject to any overriding publication right which may exist. In practice, publication right will often override the first of the bullet points listed.
This tag can be used only when the author cannot be ascertained by reasonable enquiry. If you wish to rely on it, please specify in the image description the research you have carried out to find who the author was. The above is all subject to any overriding publication right which may exist. In practice, publication right will often override the first of the bullet points listed.
Relevante Bilder
Relevante Artikel
ZweitaktmotorEin Zweitaktmotor ist ein Hubkolbenmotor, der aus der Verbrennung von Kraftstoff mechanische Leistung erzielt. Ein Arbeitsspiel währt eine Kurbelwellen-umdrehung, also zwei Takte. Wie ein Viertaktmotor kann er als Otto- oder Diesel-Motor arbeiten. Der umgangssprachliche Begriff „Zweitakter“ bezeichnet im Alltag einen ventil-losen Ottomotor mit Gemischschmierung und Zündkerze(n), der nach dem Zweitaktprinzip arbeitet; die meisten Zweitaktmotoren sind einfach und kostengünstig, zudem haben sie ein geringes Leistungsgewicht. .. weiterlesen
VerbrennungsmotorEin Verbrennungsmotor, in der Patentliteratur auch als Brennkraftmaschine bezeichnet, ist eine Wärmekraftmaschine nach dem Prinzip der Verbrennungskraftmaschine, die chemische Energie durch Treibstoff-Verbrennung in mechanische Arbeit umwandelt. Dazu wird in einem Brennraum ein zündfähiges Gemisch aus Kraftstoff und Luft (Sauerstoff) verbrannt. Kennzeichen aller Verbrennungsmotoren ist die innere Verbrennung, also die Erzeugung der Verbrennungswärme im Motor, weshalb in der englischen Sprache das Akronym ICE für Verbrennungsmotoren in Fahrzeugen verwendet wird. Die Wärmeausdehnung des so entstehenden Heißgases wird genutzt, um Kolben in Bewegung zu versetzen. Die häufigsten Arten von Verbrennungsmotoren sind Otto- (Fremdzünder) und Dieselmotoren (Selbstzünder). Eine typische Anwendung dieser Motoren ist der Antrieb von Kraftfahrzeugen wie Automobilen oder Motorrädern, Schiffen und Flugzeugen. .. weiterlesen